Google Related Exams
Professional-Cloud-DevOps-Engineer Exam







Your company stores a large volume of infrequently used data in Cloud Storage. The projects in your company's CustomerService folder access Cloud Storage frequently, but store very little data. You want to enable Data Access audit logging across the company to identify data usage patterns. You need to exclude the CustomerService folder projects from Data Access audit logging. What should you do?
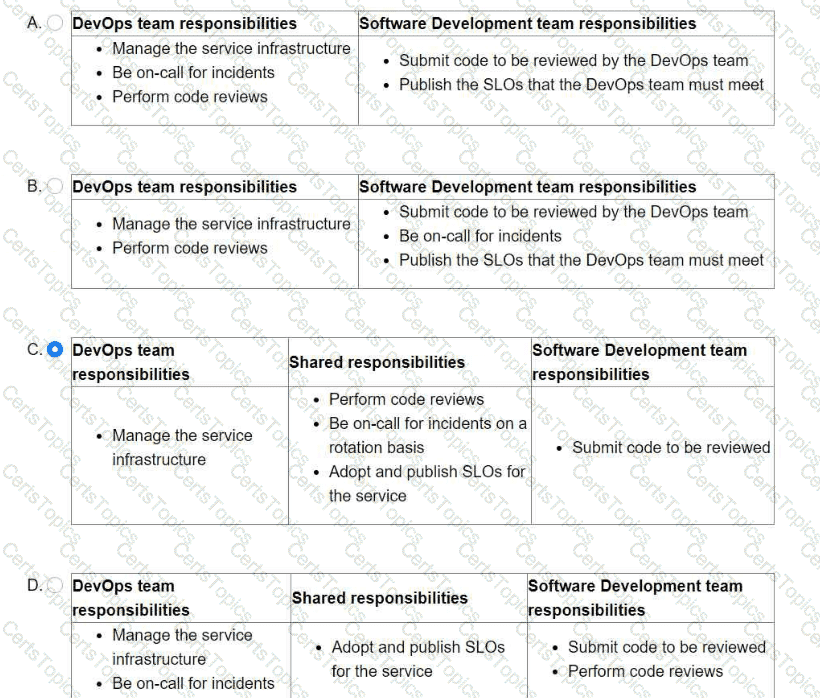
You are leading a DevOps project for your organization. The DevOps team is responsible for managing the service infrastructure and being on-call for incidents. The Software Development team is responsible for writing, submitting, and reviewing code. Neither team has any published SLOs. You want to design a new joint-ownership model for a service between the DevOps team and the Software Development team. Which responsibilities should be assigned to each team in the new joint-ownership model?
You support a production service that runs on a single Compute Engine instance. You regularly need to spend time on recreating the service by deleting the crashing instance and creating a new instance based on the relevant image. You want to reduce the time spent performing manual operations while following Site Reliability Engineering principles. What should you do?