CIW Related Exams
1D0-541 Exam







Your company must choose which type of database to use for a new project. Which of the following lists three characteristics of file-based database systems?
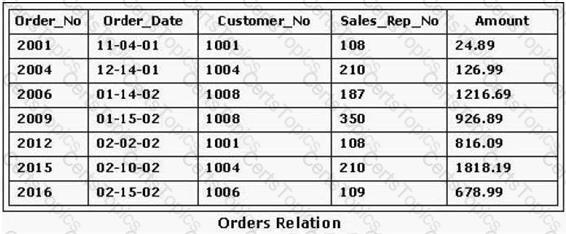
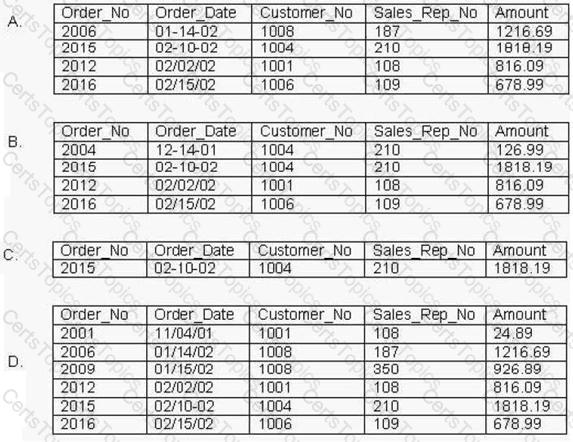
Consider the following SQL statement and the Orders relation shown in the exhibit:
What is the output of this SQL statement?
SELECT *
FROM Orders
WHERE NOT (Amount < 1000
AND Sales_Rep_No = 210);