A European car manufacturer wants to migrate its customer-facing services and its analytics platform from two on-premises data centers to the AWS Cloud. The company has a 50-mile (80.4 km) separation between its on-premises data centers and must maintain that separation between its two locations in the cloud. The company also needs failover capabilities between the two locations in the cloud.
The company's infrastructure team creates several accounts to separate workloads and responsibilities. The company provisions resources in the eu-west-3 Region and in the eu-central-1 Region. The company selects an AWS Direct Connect Partner in each Region and requests two resilient 1 Gbps fiber connections from each provider.
The company's network engineer must establish a connection between all VPCs in the accounts and between the on-premises network and the AWS Cloud. The solution must provide access to all services in both Regions in case of network issues.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company is using third-party firewall appliances to monitor and inspect traffic on premises The company wants to use this same model on AWS. The company has a single VPC with an internet gateway. The VPC has a fleet of web servers that run on Amazon EC2 instances that are managed by an Auto Scaling group.
The company's network team needs to work with the security team to establish inline inspection of all packets that are sent to and from the web servers. The solution must scale as the fleet of virtual firewall appliances scales.
Which combination of steps should the network team take to implement this solution? (Select THREE.)
A network engineer needs to deploy an AWS Network Firewall firewall into an existing AWS environment. The environment consists of the following:
A transit gateway with all VPCs attached to it
Several hundred application VPCs
A centralized egress internet VPC with a NAT gateway and an internet gateway
A centralized ingress internet VPC that hosts public Application Load Balancers
On-premises connectivity through an AWS Direct Connect gateway attachment
The application VPCs have workloads deployed across multiple Availability Zones in private subnets with the VPC route table s default route (0.0.0.0/0) pointing to the transit gateway. The Network Firewall firewall needs to inspect east-west (VPC-to-VPC) traffic and north-south (internet-bound and on-premises network) traffic by using Suricata compatible rules.
The network engineer must deploy the firewall by using a solution that requires the least possible architectural changes to the existing production environment.
Which combination of steps should the network engineer take to meet these requirements? (Choose three.)
A company uses transit gateways to route traffic between the company's VPCs. Each transit gateway has a single route table. Each route table contains attachments and routes for the VPCs that are in the same AWS Region as the transit gateway. The route tables in each VPC also contain routes to all the other VPC CIDR ranges that are available through the transit gateways. Some VPCs route to local NAT gateways.
The company plans to add many new VPCs soon. A network engineer needs a solution to add new VPC CIDR ranges to the route tables in each VPC.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST operationally efficient way?
A global delivery company is modernizing its fleet management system. The company has several business units. Each business unit designs and maintains applications that are hosted in its own AWS account in separate application VPCs in the same AWS Region. Each business unit's applications are designed to get data from a central shared services VPC.
The company wants the network connectivity architecture to provide granular security controls. The architecture also must be able to scale as more business units consume data from the central shared services VPC in the future.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST secure manner?
A network engineer is working on a large migration effort from an on-premises data center to an AWS Control Tower based multi-account environment. The environment
has a transit gateway that is deployed to a central network services account. The central network services account has been shared with an organization in AWS
Organizations through AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM).
A shared services account also exists in the environment. The shared services account hosts workloads that need to be shared with the entire organization.
The network engineer needs to create a solution to automate the deployment of common network components across the environment. The solution must provision a
VPC for application workloads to each new and existing member account. The VPCs must be connected to the transit gateway in the central network services account.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead? (Select THREE.)
Company A recently acquired Company B. Company A has a hybrid AWS and on-premises environment that uses a hosted AWS Direct Connect connection, a Direct Connect gateway, and a transit gateway. Company A has a transit VIF to access the resources in itsproduction environment in the us-east-1 Region.
Company B has applications that run across multiple VPCs in the us-west-2 Region in a single AWS account. A transit gateway connects all Company B's application VPCs. The CIDR blocks for both companies do not overlap.
Company A needs to use the existing Direct Connect connection to access Company B’s applications from the on-premises environment.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company's network engineer is designing an active-passive connection to AWS from two on-premises data centers. The company has set up AWS Direct Connect connections between the on-premises data centers and AWS. From each location, the company is using a transit VIF that connects to a Direct Connect gateway that is associated with a transit gateway.
The network engineer must ensure that traffic from AWS to the data centers is routed first to the primary data center. The traffic should be routed to the failover data center only in the case of an outage.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has multiple VPCs with subnets that use IPv4. Traffic from the VPCs to the internet uses a NAT gateway. The company wants to transition to IPv6.
A network engineer creates multiple IPv6-only subnets in an existing testing VPC. The network engineer deploys a new Amazon EC2 instance that has an IPv6 address into one of the subnets. During testing, the network engineer discovers that the new EC2 instance is not able to communicate with an IPv4-only service through the internet. The network engineer needs to enable the IPv6 EC2 instance to communicate with the IPv4-only service.
Which solution will meet this requirement?
A company is planning to host external websites on AWS. The websites will include multiple tiers such as web servers, application logic services, and databases. The company wants to use AWS Network Firewall. AWS WAR and VPC security groups for network security.
The company must ensure that the Network Firewall firewalls are deployed appropriately within relevant VPCs. The company needs the ability to centrally manage policies that are deployed to Network Firewall and AWS WAF rules. The company also needs to allow application teams to manage their own security groups while ensuring that the security groups do not allow overly permissive access.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
A development team is building a new web application in the AWS Cloud. The main company domain, example.com. is currently hosted in an Amazon Route 53 public hosted zone in one of the company's production AWS accounts.
The developers want to test the web application in the company's staging AWS account by using publicly resolvable subdomains under the example.com domain with the ability to create and delete DNS records as needed. Developers have full access to Route 53 hosted zones within the staging account, but they are prohibited from accessing resources in any of the production AWS accounts.
Which combination of steps should a network engineer take to allow the developers to create records under the example.com domain? (Select TWO.)
A company runs a workload in a single VPC on AWS. The company’s architecture contains several interface VPC endpoints for AWS services, including Amazon CloudWatch Logs and AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS). The endpoints are configured to use a shared security group. The security group is not used for any other workloads or resources.
After a security review of the environment, the company determined that the shared security group is more permissive than necessary. The company wants to make the rules associated with the security group more restrictive. The changes to the security group rules must not prevent the resources in the VPC from using AWS services through interface VPC endpoints. The changes must prevent unnecessary access.
The security group currently uses the following rules:
• Inbound - Rule 1
Protocol: TCP
Port: 443
Source: 0.0.0.0/0
• Inbound - Rule 2
Protocol: TCP
Port: 443
Source: VPC CIDR
• Outbound - Rule 1
Protocol: All
Port: All
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0
Which rule or rules should the company remove to meet with these requirements?
A company has its production VPC (VPC-A) in the eu-west-1 Region in Account 1. VPC-A is attached to a transit gateway (TGW-A) that is connected to an on-premises data center in Dublin, Ireland, by an AWS Direct Connect transit VIF that is configured for an AWS Direct Connect gateway. The company also has a staging VPC (VPC-B) that is attached to another transit gateway (TGW-B) in the eu-west-2 Region in Account 2.
A network engineer must implement connectivity between VPC-B and the on-premises data center in Dublin.
Which solutions will meet these requirements? (Choose two.)
A company is planning to use Amazon S3 to archive financial data. The data is currently stored in an on-premises data center. The company uses AWS Direct Connect with a Direct Connect gateway and a transit gateway to connect to the on-premises data center. The data cannot be transported over the public internet and must be encrypted in transit.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
AnyCompany deploys and manages networking resources in its AWS network account, named Account-A. AnyCompany acquires Example Corp, which has an application that runs behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB) in Example Corp's AWS account, named Account-B.
Example Corp needs to use AWS Global Accelerator to create an accelerator to publish the application to users. AnyCompany's networking team will manage the accelerator.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST management overhead?
A software-as-a-service (SaaS) company is migrating its private SaaS application to AWS. The company has hundreds of customers that connect to multiple data centers by using VPN tunnels. As the number of customers has grown, the company has experienced more difficulty in its effort to manage routing and segmentation of customers with complex NAT rules.
After the migration to AWS is complete, the company's AWS customers must be able to access the SaaS application directly from their VPCs. Meanwhile, the company's on-premises customers still must be able to connect through IPsec encrypted tunnels.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A real estate company is building an internal application so that real estate agents can upload photos and videos of various properties. The application will store these photos and videos in an Amazon S3 bucket as objects and will use Amazon DynamoDB to store corresponding metadata. The S3 bucket will be configured to publish all PUT events for new object uploads to an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue.
A compute cluster of Amazon EC2 instances will poll the SQS queue to find out about newly uploaded objects. The cluster will retrieve new objects, perform proprietary image and video recognition and classification update metadata in DynamoDB and replace the objects with new watermarked objects. The company does not want public IP addresses on the EC2 instances.
Which networking design solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively as application usage increases?
A company has a hybrid environment that connects an on-premises data center to the AWS Cloud. The hybrid environment uses a 10 Gbps AWS Direct Connect dedicated connection. The Direct Connect connection has multiple private VIFs that terminate in multiple VPCs.
To comply with regulations, the company must encrypt all WAN traffic, regardless of the underlying transport. The company needs to implement an encryption solution that will not affect the company's bandwidth capacity.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A Network Engineer is provisioning a subnet for a load balancer that will sit in front of a fleet of application servers in a private subnet. There is limited IP space left in the VPC CIDR. The application has few users now but is expected to grow quickly to millions of users.
What design will use the LEAST amount of IP space, while allowing for this growth?
A company wants to improve visibility into its AWS environment. The AWS environment consists of multiple VPCs that are connected to a transit gateway. The transit gateway connects to an on-premises data center through an AWS Direct Connect gateway and a pair of redundant Direct Connect connections that use transit VIFs. The company must receive notification each time a new route is advertised to AWS from on premises over Direct Connect.
What should a network engineer do to meet these requirements?
A global company runs business applications in the us-east-1 Region inside a VPC. One of the company's regional offices in London uses a virtual private gateway for an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection tom the VPC. The company has configured a transit gateway and has set up peering between the VPC and other VPCs that various departments in the company use.
Employees at the London office are experiencing latency issues when they connect to the business applications.
What should a network engineer do to reduce this latency?
A customer has set up multiple VPCs for Dev, Test, Prod, and Management. You need to set up AWS Direct Connect to enable data flow from on-premises to each VPC. The customer has monitoring software running in the Management VPC that collects metrics from the instances in all the other VPCs. Due to budget requirements, data transfer charges should be kept at minimum.
Which design should be recommended?
A company's existing AWS environment contains public application servers that run on Amazon EC2 instances. The application servers run in a VPC subnet. Each server is associated with an Elastic IP address.
The company has a new requirement for firewall inspection of all traffic from the internet before the traffic reaches any EC2 instances. A security engineer has deployed and configured a Gateway Load Balancer (GLB) in a standalone VPC with a fleet of third-party firewalls.
How should a network engineer update the environment to ensure that the traffic travels across the fleet of firewalls?
A company has a data center in the us-west-1 Region with a 10 Gbps AWS Direct Connect dedicated connection to a Direct Connect gateway. There are two private VIFs from the same data center location in us-west-1 that are attached to the same Direct Connect gateway.
VIF 1 advertises 172.16.0.0/16 with an AS PATH attribute value of 65000. VIF 2 advertises 172.16.1.0/24 with an AS PATH attribute value of 65000 65000 65000.
How will AWS route traffic to the data center for traffic that has a destination address within the 172.16.1.0/24 network range?
A company has an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection between its existing VPC and on-premises network. The default DHCP options set is associated with the VPC. The company has an application that is running on an Amazon Linux 2 Amazon EC2 instance in the VPC. The application must retrieve an Amazon RDS database secret that is stored in AWS Secrets Manager through a private VPC endpoint. An on-premises application provides internal RESTful API service that can be reached by URL Two on-premises Windows DNS servers provide internal DNS resolution.
The application on the EC2 instance needs to call the internal API service that is deployed in the on-premises environment. When the application on the EC2 instance attempts to call the internal API service by referring to the hostname that is assigned to the service, the call fails. When a network engineer tests the API service call from the same EC2 instance by using the API service's IP address, the call is successful.
What should the network engineer do to resolve this issue and prevent the same problem from affecting other resources in the VPC?
A company is using AWS Cloud WAN with one edge location in the us-east-1 Region and one edge location in the us-west-1 Region. A shared services segment exists at both edge locations. Each shared services segment has a VPC attachment to each inspection VPC in each Region. The inspection VPCs inspect traffic from a WAN by using AWS Network Firewall.
The company creates a new segment for a new business unit (BU) in the us-east-1 edge location. The new BU has three VPCs that are attached to the new BU segment. To comply with regulations, the BU VPCs must not communicate with each other. All internet-bound traffic must be inspected in the inspection VPC.
The company updates VPC route tables so any traffic that is bound for internet goes to the AWS Cloud WAN core network.
The company plans to add more VPCs for the new BU in the future. All future VPCs must comply with regulations.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST operationally efficient way? (Choose two.)
A company runs workloads in multiple VPCs in the us-east-1 Region. The VPCs are connected to a transit gateway. An AWS Direct Connect connection provides private connectivity between a data center that is in the US and the transit gateway. A Direct Connect gateway is associated with the transit gateway.
The company has recently opened a new office location in London. The company plans to launch cloud services in multiple VPCs in the eu-west-2 Region. Users in the new London office must have private access to the workloads that run in us-east-1. Users in the US data center must have access to any workloads that are created in eu-west-2. A network engineer must implement a flexible solution that provides users the required access. The solution must be able to accommodate future growth.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational effort?
A company deploys a software solution on Amazon EC2 instances that are in a clusterplacement group. The solution's UI is a single HTML page. The HTML file size is 1,024 bytes. The software processes files that exceed 1,024 MB in size. The software shares files over the network to clients upon request. The files are shared with the Don't Fragment flag set. Elastic network interfaces of the EC2 instances are set up with jumbo frames.
The UI is always accessible from all allowed source IP addresses, regardless of whether the source IP addresses are within a VPC, on the internet, or on premises. However, clients sometimes do not receive files that they request because the files fail to travel successfully from the software to the clients.
Which options provide a possible root cause of these failures? (Choose two.)
A company has workloads that run in a VPC. The workloads access Amazon S3 by using an S3 gateway endpoint. The company also has on-premises workloads that need to access Amazon
S3 privately over a VPN connection. The company has established the VPN connection to the VPC.
Which solution will provide connectivity to Amazon S3 from the VPC workloads and the on-premises workloads in the MOST operationally efficient way?
An organization launched an IPv6-only web portal to support IPv6-native mobile clients. Front-end instances launch in an Amazon VPC associated with an appropriate IPv6 CIDR. The VPC IPv4 CIDR is fully utilized. A single subnet exists in each of two Availability Zones with appropriately configured IPv6 CIDR associations. Auto Scaling is properly configured, and no Elastic Load Balancing is used.
Customers say the service is unavailable during peak load times. The network engineer attempts to launch an instance manually and receives the following message: “There are not enough free addresses in subnet ‘subnet-12345677’ to satisfy the requested number of instances.”
What action will resolve the availability problem?
An ecommerce company is hosting a web application on Amazon EC2 instances to handle continuously changing customer demand. The EC2 instances are part of an Auto Scaling group. The company wants to implement a solution to distribute traffic from customers to the EC2 instances. The company must encrypt all traffic at all stages between the customers and the application servers. No decryption at intermediate points is allowed.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A finance company runs multiple applications on Amazon EC2 instances in two VPCs that are within a single AWS Region. The company uses one VPC for stock trading applications. The company uses the second VPC for financial applications. Both VPCs are connected to a transit gateway that is configured as a multicast router.
In the stock trading VPC, an EC2 instance that has an IP address of 10.128.10.2 sends trading data over a multicast network to the 239.10.10.10 IP address on UDP Port 5102. The company recently launched two new EC2 instances in the financial application VPC. The new EC2 instances need to receive the multicast stock trading data from the EC2 instance that is in the stock trading VPC.
Which combination of steps should the company take to meet this requirement? (Choose three.)
A company's network engineer is configuring an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection between a transit gateway and the company's on-premises network. The Site-to-Site VPN connection is configured to use BGP over two tunnels in active/active mode with equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing activated on the transit gateway.
When the network engineer attempts to send traffic from the on-premises network to an Amazon EC2 instance, traffic is sent over the first tunnel. However, return traffic is received over the second tunnel and is dropped at the customer gateway. The network engineer must resolve this issue without reducing the overall VPN bandwidth.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has critical VPC workloads that connect to an on-premises data center through two redundant active-passive AWS Direct Connect connections. However, a recent outage on one Direct Connect connection revealed that it takes more than a minute for traffic to fail over to the secondary Direct Connect connection. The company wants to reduce the failover time from minutes to seconds.
Which solution will provide the LARGEST reduction in the BGP failover time?
A company has an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection between AWS and its branch office. A network engineer is troubleshooting connectivity issues that the connection is experiencing. The VPN connection terminates at a transit gateway and is statically routed. In the transit gateway route table, there are several static route entries that target specific subnets at the branch office.
The network engineer determines that the root cause of the issues was the expansion of underlying subnet ranges in the branch office during routine maintenance.
Which solution will solve this problem with the LEAST administrative overhead for future expansion efforts?
A company has an internal web-based application that employees use. The company hosts the application over a VPN in the company's on-premises network. The application runs on a fleet of Amazon EC2 instances in a private subnet behind a Network Load Balancer (NLB) in the same subnet. The instances are in an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group.
During a recent security incident, SQL injection occurred on the application. A network engineer must implement a solution to prevent SQL injection attacks in the future.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements? (Select THREE.)
A company's application is deployed on Amazon EC2 instances in a single VPC in an AWS Region. The EC2 instances are running in two Availability Zones. The company decides to use a fleet of traffic inspection instances from AWS Marketplace to inspect traffic between the VPC and the internet. The company is performing tests before the company deploys the architecture into production.
The fleet is located in a shared inspection VPC behind a Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB). To minimize the cost of the solution, the company deployed only one inspection instance in each Availability Zone that the application uses.
During tests, a network engineer notices that traffic inspection works as expected when the network is stable. However, during maintenance of the inspection instances, the internet sessions time out for some application instances. The application instances are not able to establish new sessions.
Which combination of steps will remediate these issues? (Choose two.)
A company is growing rapidly. Data transfers between the company's on-premises systems and Amazon EC2 instances that run in VPCs are limited by the throughput of a single AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection between the company's on-premises data center firewall and an AWS Transit Gateway.
A network engineer must resolve the throttling by designing a solution that is highly available and secure. The solution also must scale the VPN throughput from on premises to the VPC resources to support the increase in traffic.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
An Australian ecommerce company hosts all of its services in the AWS Cloud and wants to expand its customer base to the United States (US). The company is targeting the western US for the expansion.
The company’s existing AWS architecture consists of four AWS accounts with multiple VPCs deployed in the ap-southeast-2 Region. All VPCs are attached to a transit gateway in ap-southeast-2. There are dedicated VPCs for each application service. The company also has VPCs for centralized security features such as proxies, firewalls, and logging.
The company plans to duplicate the infrastructure from ap-southeast-2 to the us-west-1 Region. A network engineer must establish connectivity between the various applications in the two Regions. The solution must maximize bandwidth, minimize latency and minimize operational overhead.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company is deploying third-party firewall appliances for traffic inspection and NAT capabilities in its VPC. The VPC is configured with private subnets and public subnets. The company needs to deploy the firewall appliances behind a load balancer.
Which architecture will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A company uses Amazon Route 53 for its DNS needs. The company's security team wants to update the DNS infrastructure to provide the most recent security posture.
The security team has configured DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) for the domain. The security team wants a network engineer to explain who is responsible for the
rotation of DNSSEC keys.
Which explanation should the network administrator provide to the security team?
A company recently implemented a security policy that prohibits developers from launching VPC network infrastructure. The policy states that any time a NAT gateway is launched in a VPC, the company's network security team must immediately receive an alert to terminate the NAT gateway. The network security team needs to implement a solution that can be deployed across AWS accounts with the least possible administrative overhead. The solution also must provide the network security team with a simple way to view compliance history.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company is planning to use an AWS Transit Gateway hub and spoke architecture to migrate to AWS. The current on-premises multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) network has strict controls that enforce network segmentation by using MPLS VPNs. The company has provisioned two 10 Gbps AWS Direct Connect connections to provide resilient, high-speed, low-latency connectivity to AWS.
A security engineer needs to apply the concept of network segmentation to the AWS environment to ensure that virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) is logically separated for each of the company's software development environments. The number of MPLS VPNs will increase in the future. On-premises MPLS VPNs will have overlapping address space. The company's AWS network design must support overlapping address space for the VPNs.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A network engineer is designing hybrid connectivity with AWS Direct Connect and AWS Transit Gateway. A transit gateway is attached to a Direct Connect gateway and 19 VPCs across different AWS accounts. Two new VPCs are being attached to the transit gateway. The IP address administrator has assigned 10.0.32.0/21 to the first VPC and 10.0.40.0/21 to the second VPC. The prefix list has one CIDR block remaining before the prefix list reaches the quota for the maximum number of entries.
What should the network engineer do to advertise the routes from AWS to on premises to meet these requirements?
A company is planning a migration of its critical workloads from an on-premises data center to Amazon EC2 instances. The plan includes a new 10 Gbps AWS Direct Connect dedicated connection from the on-premises data center to a VPC that is attached to a transit gateway. The migration must occur over encrypted paths between the on-premises data center and the AWS Cloud.
Which solution will meet these requirements while providing the HIGHEST throughput?
A company is hosting an application on Amazon EC2 instances behind a Network Load Balancer (NLB). A solutions architect added EC2 instances in a second Availability Zone to improve the availability of the application. The solutions architect added the instances to the NLB target group.
The company's operations team notices that traffic is being routed only to the instances in the first Availability Zone.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution to resolve this issue?
A company's application team is unable to launch new resources into its VPC. A network engineer discovers that the VPC has run out of usable IP addresses. The VPC CIDR block is 172.16.0.0/16.
Which additional CIDR block can the network engineer attach to the VPC?
A company has a total of 30 VPCs. Three AWS Regions each contain 10 VPCs. The company has attached the VPCs in each Region to a transit gateway in that Region. The company also
has set up inter-Region peering connections between the transit gateways.
The company wants to use AWS Direct Connect to provide access from its on-premises location for only four VPCs across the three Regions. The company has provisioned four Direct
Connect connections at two Direct Connect locations.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively? (Select THREE.)
A company has deployed an AWS Network Firewall firewall into a VPC. A network engineer needs to implement a solution to deliver Network Firewall flow logs to the company’s Amazon OpenSearch Service (Amazon Elasticsearch Service) cluster in the shortest possible time.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has configured an AWS Cloud WAN core network with edge locations in the us-east-1 Region and the us-west-1 Region. Each edge location has two segments: development and staging. The segments use the default core network policy.
The company has attached VPCs to the core network. A development VPC is attached to the development segment in us-east-1 and is configured to use the 10.0.0.0/16 CIDR block. A staging VPC is attached to the staging segment in us-west-1 and is configured to use the 10.5.0.0/16 CIDR block. The company has updated the route tables for both VPCs with a route that directs any traffic for 0.0.0.0/0 to the core network.
The company’s network team needs to establish communication between the two VPCs by using the AWS Cloud WAN core network. The network team is not receiving a response during tests of communication between the VPCs. The network team has verified that security groups and network ACLs are not blocking the traffic.
What should the network team do to establish this communication?
A company plans to run a computationally intensive data processing application on AWS. The data is highly sensitive. The VPC must have no direct internet access, and the company has applied strict network security to control access.
Data scientists will transfer data from the company's on-premises data center to the instances by using an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection. The on-premises data center uses the network range 172.31.0.0/20 and will use the network range 172.31.16.0/20 in the application VPC.
The data scientists report that they can start new instances of the application but that they cannot transfer any data from the on-premises data center. A network engineer enables VPC flow logs and sends a ping to one of the instances to test reachability. The flow logs show the following:
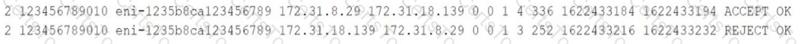
The network engineer must recommend a solution that will give the data scientists the ability to transfer data from the on-premises data center.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has a transit gateway in a single AWS account. The company sends flow logs for the transit gateway to an Amazon CloudWatch Logs log group.
The company created an AWS Lambda function to analyze the logs. The Lambda function sends a notification to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic when a VPC generates traffic that is dropped by the transit gateway. Each notification contains the account ID. VPC ID, and total amount of dropped packets.
The company wants to subscribe a new Lambda function to the SNS topic. The new Lambda function must automatically prevent the traffic that is identified in each notification from leaving a VPC by applying a network ACL to the transit gateway attachment subnets in the VPC that generates the traffic.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has a public application. The application uses an Application Load Balancer (ALB) that has a target group of Amazon EC2 instances.
The company wants to protect the application from security issues in web requests. The traffic to the application must have end-to-end encryption.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company needs to transfer data between its VPC and its on-premises data center. The data must travel through a connection that has dedicated bandwidth. The data also must be encrypted in transit. The company has been working with an AWS Partner Network(APN) Partner to establish the connection.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements? (Choose three.)
A company uses an AWS Direct Connect private VIF with a link aggregation group (LAG) that consists of two 10 Gbps connections. The company's security team has implemented a new requirement for external network connections to provide layer 2 encryption. The company's network team plans to use MACsec support for Direct Connect to meet the new requirement.
Which combination of steps should the network team take to implement this functionality? (Choose three.)
A company has deployed Amazon EC2 instances in private subnets in a VPC. The EC2 instances must initiate any requests that leave the VPC, including requests to the company's on-premises data center over an AWS Direct Connect connection. No resources outside the VPC can be allowed toopen communications directly to the EC2 instances.
The on-premises data center's customer gateway is configured with a stateful firewall device that filters for incoming and outgoing requests to and from multiple VPCs. In addition, the company wants to use a single IP match rule to allow all the communications from the EC2 instances to its data center from a single IP address.
Which solution will meet these requirements with the LEAST amount of operational overhead?
A company is deploying a new application in the AWS Cloud. The company wants a highly available web server that will sit behind an Elastic Load Balancer. The load balancer will route requests to multiple target groups based on the URL in the request. All traffic must use HTTPS. TLS processing must be offloaded to the load balancer. The web server must know the user’s IP address so that the company can keep accurate logs for security purposes.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has multiple AWS accounts. Each account contains one or more VPCs. A new security guideline requires the inspection of all traffic between VPCs.
The company has deployed a transit gateway that provides connectivity between all VPCs. The company also has deployed a shared services VPC with Amazon EC2 instances that include IDS services for stateful inspection. The EC2 instances are deployed across three Availability Zones. The company has set up VPC associations and routing on the transit gateway. The company has migrated a few test VPCs to the new solution for traffic inspection.
Soon after the configuration of routing, the company receives reports of intermittent connections for traffic that crosses Availability Zones.
What should a network engineer do to resolve this issue?
A company uses a 1 Gbps AWS Direct Connect connection to connect its AWS environment to its on-premises data center. The connection provides employees with access to an application VPC that is hosted on AWS. Many remote employees use a company-provided VPN to connect to the data center. These employees are reporting slowness when they access the application during business hours. On-premises users have started to report similar slowness while they are in the office.
The company plans to build an additional application on AWS. On-site and remote employees will use the additional application. After the deployment of this additional application, the company will need 20% more bandwidth than the company currently uses. With the increased usage, the company wants to add resiliency to the AWS connectivity. A network engineer must review the current implementation and must make improvements within a limited budget.
What should the network engineer do to meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A company's VPC has Amazon EC2 instances that are communicating with AWS services over the public internet. The company needs to change the connectivity so that the communication
does not occur over the public intemet.
The company deploys AWS PrivateLink endpoints in the VPC. After the deployment of the PrivateLink endpoints, the EC2 instances can no longer communicate at all with the required AWS
services.
Which combination of steps should a network engineer take to restore communicationwith the AWS services? (Select TWO.)
A network engineer needs to set up an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group to run a Linux-based network appliance in a highly available architecture. The network engineer is configuring the new launch template for the Auto Scaling group.
In addition to the primary network interface the network appliance requires a second network interface that will be used exclusively by the application to exchange traffic with hosts over the internet. The company has set up a Bring Your Own IP (BYOIP) pool that includes an Elastic IP address that should be used as the public IP address for the second network interface.
How can the network engineer implement the required architecture?
A company has an AWS account with four VPCs in the us-east-1 Region. The VPCs consist of a development VPC and three production VPCs that host various workloads.
The company has extended its on-premises data center to AWS with AWS Direct Connect by using a Direct Connect gateway. The company now wants to establish connectivity to its production VPCs and development VPC from on premises. The production VPCs are allowed to route data to each other. However, the development VPC must be isolated from the production VPCs. No data can flow between the development VPC and the production VPCs.
In preparation to implement this solution, a network engineer creates a transit gateway with a single transit gateway route table. Default route table association and default route table propagation are turned off. The network engineer attaches the production VPCs. the development VPC. and the Direct Connect gateway to the transit gateway. For each VPC route table, the network engineer adds a route to 0.0.0.0/0 with the transit gateway as the next destination.
Which combination of steps should the network engineer take next to complete this solution? (Select THREE.)
A company wants to implement a distributed architecture on AWS that uses a Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) and GWLB endpoints.
The company has chosen a hub-and-spoke model. The model includes a GWLB and virtual appliances that are deployed into a centralized appliance VPC and GWLB endpoints. The model also includes internet gateways that are configured in spoke VPCs.
Which sequence of traffic flow to the internet from the spoke VPC is correct?
A company needs to manage Amazon EC2 instances through command line interfaces for Linux hosts and Windows hosts. The EC2 instances are deployed in an environment in which there is
no route to the internet. The company must implement role-based access control for management of the instances. The company has a standalone on-premises environment.
Which approach will meet these requirements with the LEAST maintenance overhead?
A company is using an Amazon CloudFront distribution that is configured with an Application Load Balancer (ALB) as an origin. A network engineer needs to implement a solution that requires
all inbound traffic to the ALB to come from CloudFront. The network engineer must implement the solution at the network layer rather than in the application.
Which solution will meet these requirements in the MOST operationally efficient way?
A network engineer must provide additional safeguards to protect encrypted data at ApplicationLoad Balancers (ALBs) through the use of a unique random session key.
What should the network engineer do to meet this requirement?
A retail company is running its service on AWS. The company’s architecture includes Application Load Balancers (ALBs) in public subnets. The ALB target groups are configured to send traffic tobackend Amazon EC2 instances in private subnets. These backend EC2 instances can call externally hosted services over the internet by using a NAT gateway.
The company has noticed in its billing that NAT gateway usage has increased significantly. A network engineer needs to find out the source of this increased usage.
Which options can the network engineer use to investigate the traffic through the NAT gateway? (Choose two.)
A global company is establishing network connections between the company's primary and secondary data centers and a VPC. A network engineer needs to maximize resiliency and fault tolerance for the connections. The network bandwidth must be greater than 10 Gbps.
Which solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
A company has deployed a software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) solution to interconnect all of its offices. The company is migrating workloads to AWS and needs to extend its SD-WAN solution to support connectivity to these workloads.
A network engineer plans to deploy AWS Transit Gateway Connect and two SD-WAN virtual appliances to provide this connectivity. According to company policies, only a single SD-WAN virtual appliance can handle traffic from AWS workloads at a given time.
How should the network engineer configure routing to meet these requirements?
A company has a transit gateway in AWS Account A. The company uses AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) to share the transit gateway so that users in other accounts can connect to multiple VPCs in the same AWS Region. AWS Account B contains a VPC (10.0.0.0/16) with subnet 10.0.0.0/24 in the us-west-2a Availability Zone and subnet 10.0.1.0/24 in the us-west-2b Availability Zone. Resources in these subnets can communicate with other VPCs.
A network engineer creates two new subnets: 10.0.2.0/24 in the us-west-2b Availability Zone and 10.0.3.0/24 in the us-west-2c Availability Zone. All the subnets share one route table. The default route 0.0.0.0/0 is pointing to the transit gateway. Resources in subnet 10.0.2.0/24 can communicate with other VPCs, but resources in subnet 10.0.3.0/24 cannot communicate with other VPCs.
What should the network engineer do so that resources in subnet 10.0.3.0/24 can communicate with other VPCs?
A company is developing a new application that is deployed in multiple VPCs across multiple AWS Regions. The VPCs are connected through AWS Transit Gateway. The VPCs contain private subnets and public subnets.
All outbound internet traffic in the private subnets must be audited and logged. The company's network engineer plans to use AWS Network Firewall and must ensure that all traffic through Network Firewall is completely logged for auditing and alerting.
How should the network engineer configure Network Firewall logging to meet these requirements?
A company is migrating an application from on premises to AWS. The company will host the application on Amazon EC2 instances that are deployed in a single VPC. During the migration period, DNS queries from the EC2 instances must be able to resolve names of on-premises servers. The migration is expected to take 3 months After the 3-month migration period, the resolution of on-premises servers will no longer be needed.
What should a network engineer do to meet these requirements with the LEAST amount of configuration?
A company's development team has created a new product recommendation web service. The web service is hosted in a VPC with a CIDR block of 192.168.224.0/19. The company has deployed the web service on Amazon EC2 instances and has configured an Auto Scaling group as the target of a Network Load Balancer (NLB).
The company wants to perform testing to determine whether users who receive product recommendations spend more money than users who do not receive product recommendations. The company has a big sales event in 5 days and needs to integrate its existing production environment with the recommendation engine by then. The existing production environment is hosted in a VPC with a CIDR block of 192.168.128 0/17.
A network engineer must integrate the systems by designing a solution that results in the least possible disruption to the existing environments.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company is deploying a new application on AWS. The application uses dynamic multicasting. The company has five VPCs that are all attached to a transit gateway Amazon EC2 instances in each VPC need to be able to register dynamically to receive a multicast transmission.
How should a network engineer configure the AWS resources to meet these requirements?
A company has deployed a web application on AWS. The web application uses an Application Load Balancer (ALB) across multiple Availability Zones. The targets of the ALB are AWS Lambda functions. The web application also uses Amazon CloudWatch metrics for monitoring.
Users report that parts of the web application are not loading properly. A network engineer needs to troubleshoot the problem. The network engineer enables access logging for the ALB.
What should the network engineer do next to determine which errors the ALB is receiving?
A company has an application that runs on premises. The application needs to communicate with an application that runs in a VPC on AWS. The communication between the applications must be encrypted and must use private IP addresses. The communication cannot travel across the public internet.
The company has established a 1 Gbps AWS Direct Connect connection between the on-premises location and AWS.
Which solution will meet the connectivity requirements with the LEAST operational overhead?
A company runs an application on Amazon EC2 instances. A network engineer implements a NAT gateway in the application's VPC to replace self-managed NAT instances. After the network engineer shifts traffic from the self-managed NAT instances to the NAT gateway, users begin to report issues.
During troubleshooting, the network engineer discovers that the connection to the application is closing after approximately 6 minutes of inactivity.
What should the network engineer do to resolve this issue?
A company has a VPC in the AWS Cloud. The company recently acquired a competitor that also has a VPC in the AWS Cloud. A network engineer discovers an IP address overlap between the two VPCs. Both VPCs require access to an AWS Marketplace partner service.
Which solution will ensure interoperability among the VPC hosted services and the AWS Marketplace partner service?
Your company runs an application for the US market in the us-east-1 AWS region. This application uses proprietary TCP and UDP protocols on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances. End users run a real-time, front-end application on their local PCs. This front-end application knows the DNS hostname of the service.
You must prepare the system for global expansion. The end users must access the application with lowest latency.
How should you use AWS services to meet these requirements?
A company’s data center is connected to a single AWS Region by an AWS Direct Connect dedicated connection. The company has a single VPC in the Region. The company stores logs for all its applications locally in the data center.
The company must keep all application logs for 7 years. The company decides to copy all application logs to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
A company has a VPC that includes application workloads that run on Amazon EC2 instances in a single AWS Region. The company wants to use AWS Local Zones to deploy an extension of the application workloads that run in the Region. The extended workloads in the Local Zone need to communicate bidirectionally with the workloads in the VPC in the Region.
Which solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
An education agency is preparing for its annual competition between schools. In the competition, students at schools from around the country solve math problems, complete puzzles, and write essays.
The IP addressing plan of all the schools is well-known and is administered centrally. The competition is hosted in the AWS Cloud and is not publicly available. All competition traffic must be encrypted in transit. Only authorized endpoints can access the competition. All the schools have firewall policies that block ICMP traffic.
A network engineer builds a solution in which all the schools access the competition through AWS Site-to-Site VPN connections. The network engineer uses BGP as the routing protocol. The network engineer must implement a solution that notifies schools when they lose connectivity and need to take action on their premises to address the issue.
Which combination of steps will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively? (Choose two.)
A company is running multiple workloads on Amazon EC2 instances in public subnets. In a recent incident, an attacker exploited an application vulnerability on one of the EC2 instances to gain access to the instance. The company fixed the application and launched a replacement EC2 instance that contains the updated application.
The attacker used the compromised application to spread malware over the internet. The company became aware of the compromise through a notification from AWS. The company needs the ability to identify when an application that is deployed on an EC2 instance is spreading malware.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational effort?
An IoT company sells hardware sensor modules that periodically send out temperature, humidity, pressure, and location data through the MQTT messaging protocol. The hardware sensor modules send this data to the company's on-premises MQTT brokers that run on Linux servers behind a load balancer. The hardware sensor modules have been hardcoded with public IP addresses to reach the brokers.
The company is growing and is acquiring customers across the world. The existing solution can no longer scale and is introducing additional latency because of the company's global presence. As a result, the company decides to migrate its entire infrastructure from on premises to the AWS Cloud. The company needs to migrate without reconfiguring the hardware sensor modules that are already deployed across the world. The solution also must minimize latency.
The company migrates the MQTT brokers to run on Amazon EC2 instances.
What should the company do next to meet these requirements?