ASQ Related Exams
CMQ-OE Exam







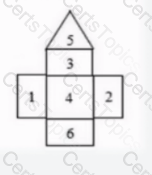
The house of quality pictured above was designed for product planning and development to specific customer wants and needs, which of the following sections would contain the planning matrix that lists market research and strategic planning?
When a project requires collaboration among different functional areas, the first step for the project manager should be to