UiPath Related Exams
UiPath-SAIv1 Exam







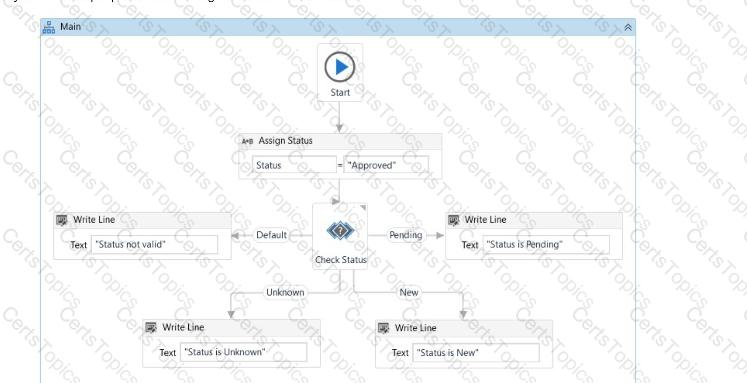
What will be displayed in the Output panel after running the workflow below?
What function in the train.py file is responsible for persisting the trained model?