HipLocal wants to reduce the number of on-call engineers and eliminate manual scaling.
Which two services should they choose? (Choose two.)
Which database should HipLocal use for storing user activity?
In order to meet their business requirements, how should HipLocal store their application state?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
A recent security audit discovers that HipLocal’s database credentials for their Compute Engine-hosted MySQL databases are stored in plain text on persistent disks. HipLocal needs to reduce the risk of these credentials being stolen. What should they do?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal is expanding into new locations. They must capture additional data each time the application is launched in a new European country. This is causing delays in the development process due to constant schema changes and a lack of environments for conducting testing on the application changes. How should they resolve the issue while meeting the business requirements?
HipLocal wants to improve the resilience of their MySQL deployment, while also meeting their business and technical requirements.
Which configuration should they choose?
Which service should HipLocal use to enable access to internal apps?
HipLocal's APIs are showing occasional failures, but they cannot find a pattern. They want to collect some
metrics to help them troubleshoot.
What should they do?
Which service should HipLocal use for their public APIs?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal's application uses Cloud Client Libraries to interact with Google Cloud. HipLocal needs to configure authentication and authorization in the Cloud Client Libraries to implement least privileged access for the application. What should they do?
HipLocal’s data science team wants to analyze user reviews.
How should they prepare the data?
HipLocal's.net-based auth service fails under intermittent load.
What should they do?
For this question refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal wants to reduce the latency of their services for users in global locations. They have created read replicas of their database in locations where their users reside and configured their service to read traffic using those replicas. How should they further reduce latency for all database interactions with the least amount of effort?
HipLocal is configuring their access controls.
Which firewall configuration should they implement?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
How should HipLocal increase their API development speed while continuing to provide the QA team with a stable testing environment that meets feature requirements?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
How should HipLocal redesign their architecture to ensure that the application scales to support a large increase in users?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
Which Google Cloud product addresses HipLocal’s business requirements for service level indicators and objectives?
In order for HipLocal to store application state and meet their stated business requirements, which database service should they migrate to?
HipLocal has connected their Hadoop infrastructure to GCP using Cloud Interconnect in order to query data stored on persistent disks.
Which IP strategy should they use?
Your team detected a spike of errors in an application running on Cloud Run in your production project. The application is configured to read messages from Pub/Sub topic A, process the messages, and write the messages to topic B. You want to conduct tests to identify the cause of the errors. You can use a set of mock messages for testing. What should you do?
You support an application that uses the Cloud Storage API. You review the logs and discover multiple HTTP 503 Service Unavailable error responses from the API. Your application logs the error and does not take any further action. You want to implement Google-recommended retry logic to improve success rates. Which approach should you take?
Before promoting your new application code to production, you want to conduct testing across a variety of different users. Although this plan is risky, you want to test the new version of the application with production users and you want to control which users are forwarded to the new version of the application based on their operating system. If bugs are discovered in the new version, you want to roll back the newly deployed version of the application as quickly as possible.
What should you do?
You have an application deployed in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You need to update the application to make authorized requests to Google Cloud managed services. You want this to be a one-time setup, and you need to follow security best practices of auto-rotating your security keys and storing them in an encrypted store. You already created a service account with appropriate access to the Google Cloud service. What should you do next?
You are developing an application that reads credit card data from a Pub/Sub subscription. You have written code and completed unit testing. You need to test the Pub/Sub integration before deploying to Google Cloud. What should you do?
You have an application running in a production Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. You use Cloud Deploy to automatically deploy your application to your production GKE cluster. As part of your development process: you are planning to make frequent changes to the applications source code and need to select the tools to test the changes before pushing them to your remote source code repository. Your toolset must meet the following requirements:
• Test frequent local changes automatically.
• Local deployment emulates production deployment.
Which tools should you use to test building and running a container on your laptop using minimal resources'?
You are configuring a continuous integration pipeline using Cloud Build to automate the deployment of new container images to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The pipeline builds the application from its source code, runs unit and integration tests in separate steps, and pushes the container to Container Registry. The application runs on a Python web server.
The Dockerfile is as follows:
FROM python:3.7-alpine -
COPY . /app -
WORKDIR /app -
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD [ "gunicorn", "-w 4", "main:app" ]
You notice that Cloud Build runs are taking longer than expected to complete. You want to decrease the build time. What should you do? (Choose two.)
You have recently instrumented a new application with OpenTelemetry, and you want to check the latency of your application requests in Trace. You want to ensure that a specific request is always traced. What should you do?
Your company’s corporate policy states that there must be a copyright comment at the very beginning of all source files. You want to write a custom step in Cloud Build that is triggered by each source commit. You need the trigger to validate that the source contains a copyright and add one for subsequent steps if not there. What should you do?
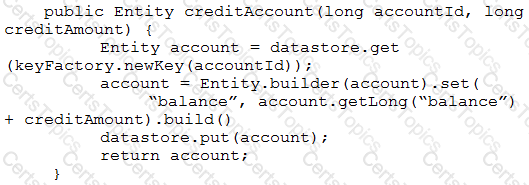
Your teammate has asked you to review the code below, which is adding a credit to an account balance in Cloud Datastore. Which improvement should you suggest your teammate make?
Your development team has been asked to refactor an existing monolithic application into a set of composable microservices. Which design aspects should you implement for the new application? (Choose two.)
You are using Cloud Run to host a web application. You need to securely obtain the application project ID and region where the application is running and display this information to users. You want to use the most performant approach. What should you do?
You recently developed a new application. You want to deploy the application on Cloud Run without a Dockerfile. Your organization requires that all container images are pushed to a centrally managed container repository. How should you build your container using Google Cloud services? (Choose two.)
You are developing a marquee stateless web application that will run on Google Cloud. The rate of the incoming user traffic is expected to be unpredictable, with no traffic on some days and large spikes on other days. You need the application to automatically scale up and down, and you need to minimize the cost associated with running the application. What should you do?
You want to migrate an on-premises container running in Knative to Google Cloud. You need to make sure that the migration doesn't affect your application's deployment strategy, and you want to use a fully managed service. Which Google Cloud service should you use to deploy your container?
Your team is developing an ecommerce platform for your company. Users will log in to the website and add items to their shopping cart. Users will be automatically logged out after 30 minutes of inactivity. When users log back in, their shopping cart should be saved. How should you store users’ session and shopping cart information while following Google-recommended best practices?
You are deploying your application to a Compute Engine virtual machine instance. Your application is
configured to write its log files to disk. You want to view the logs in Stackdriver Logging without changing the
application code.
What should you do?
You are developing an application that will handle requests from end users. You need to secure a Cloud Function called by the application to allow authorized end users to authenticate to the function via the application while restricting access to unauthorized users. You will integrate Google Sign-In as part of the solution and want to follow Google-recommended best practices. What should you do?
Your data is stored in Cloud Storage buckets. Fellow developers have reported that data downloaded from Cloud Storage is resulting in slow API performance. You want to research the issue to provide details to the GCP support team. Which command should you run?
You recently developed an application. You need to call the Cloud Storage API from a Compute Engine instance that doesn’t have a public IP address. What should you do?
Your application is logging to Stackdriver. You want to get the count of all requests on all /api/alpha/*
endpoints.
What should you do?