Which of the following factors can cause obligors to default at the same time?
I. Obligors may be harmed by exposures to similar risk factors simultaneously.
II. Obligors may exhibit herd behavior.
III. Obligors may be subject to the sampling bias.
IV. Obligors may exhibit speculative bias.
Which one of the following four statements regarding counterparty credit risk is INCORRECT?
Which one of the following changes would typically increase the price of a fixed income instrument, such as a bond?
Which one of the following four mathematical option pricing models is used most widely for pricing European options?
Which one of the following four options is NOT a typical component of a currency swap?
The value of which one of the following four option types is typically dependent on both the final price of its underlying asset and its own price history?
Alpha Bank determined that Delta Industrial Machinery Corporation has 2% change of default on a one-year no-payment of USD $1 million, including interest and principal repayment. The bank charges 3% interest rate spread to firms in the machinery industry, and the risk-free interest rate is 6%. Alpha Bank receives both interest and principal payments once at the end the year. Delta can only default at the end of the year. If Delta defaults, the bank expects to lose 50% of its promised payment. What interest rate should Alpha Bank charge on the no-payment loan to Delta Industrial Machinery Corporation?
After entering the securitization business, Delta Bank increases its cash efficiency by selling off the lower risk portions of the portfolio credit risk. This process ___ risk on the residual pieces of the credit portfolio, and as a result it ___ return on equity for the bank.
Which one of the following four statements about the relationship between exchange rates and option values is correct?
To estimate the interest charges on the loan, an analyst should use one of the following four formulas:
Which one of the following four statements correctly describes an American call option?
Which one of the following four alternatives lists the three most widely traded currencies on the global foreign exchange market, as of April 2007, in the decreasing order of market share? EUR is the abbreviation of the European euro, JPY is for the Japanese yen, and USD is for the United States dollar, respectively.
A financial analyst is trying to distinguish credit risk from market risk. A $100 loan collateralized with $200 in stock has limited ___, but an uncollateralized obligation issued by a large bank to pay an amount linked to the long-term performance of the Nikkei 225 Index that measures the performance of the leading Japanese stocks on the Tokyo Stock Exchange likely has more ___ than ___.
Changes to which one of the following four factors would typically not increase the cost of credit?
Which one of the following four global markets for financial assets or instruments is widely believed to be the most liquid?
Which one of the following four statements does identify correctly the relationship between the value of an option and perceived exchange rate volatility?
Which of the following statements regarding bonds is correct?
I. Interest rates on bonds are typically stated on an annualized rate.
II. Bonds can pay floating coupons that are directly linked to various interest rate indices.
III. Convertible bonds have an element of prepayment risk.
IV. Callable bonds have an element of equity risk.
Which one of the following four statements on factors affecting the value of options is correct?
Except for the credit quality of the Credit Default Swap protection seller, the following relationship correctly approximates the yield on a risk-free instrument:
What is generally true of the relationship between a bond's yield and it's time to maturity when the yield curve is upward sloping?
The pricing of credit default swaps is a function of all of the following EXCEPT:
In the United States, foreign exchange derivative transactions typically occur between
When looking at the distribution of portfolio credit losses, the shape of the loss distribution is ___ , as the likelihood of total losses, the sum of expected and unexpected credit losses, is ___ than the likelihood of no credit losses.
By foreign exchange market convention, spot foreign exchange transactions are to be exchanged at the spot date based on the following settlement rule:
What is the explanation offered by the liquidity preference theory for the upward sloping yield curve shape?
Which one of the following four model types would assign an obligor to an obligor class based on the risk characteristics of the borrower at the time the loan was originated and estimate the default probability based on the past default rate of the members of that particular class?
Counterparty credit risk assessment differs from traditional credit risk assessment in all of the following features EXCEPT:
Which one of the following four variables of the Black-Scholes model is typically NOT known at a point in time?
Which one of the following four options does NOT represent a benefit of compensating balances to the bank?
A bank customer chooses a mortgage with low initial payments and payments that increase over time because the customer knows that she will have trouble making payments in the early years of the loan. The bank makes this type of mortgage with the same default assumptions uses for ordinary mortgages, thus underestimating the risk of default and becoming exposed to:
Which one of the following four statements correctly defines chooser options?
Gamma Bank is active in loan underwriting and securitization business, and given its collective credit exposure, it will be typically most interested in the following types of portfolio credit risk:
I. Expected loss
II. Duration
III. Unexpected loss
IV. Factor sensitivities
A credit associate extending a loan to an obligor suspects that the obligor may change his behavior after the loan has been originated. The obligor in this case may use the loan proceeds for purposes not sanctioned by the lender, thereby increasing the risk of default. Hence, the credit associate must estimate the probability of default based on the assumptions about the applicability of the following tendency to this lending situation:
To safeguard its capital and obtain insurance if the borrowers cannot repay their loans, Gamma Bank accepts financial collateral to manage its credit risk and mitigate the effect of the borrowers' defaults. Gamma Bank will typically accept all of the following instruments as financial collateral EXCEPT?
To estimate a partial change in option price, a risk manager will use the following formula:
In the United States, during the second quarter of 2009, transactions in foreign exchange derivative contracts comprised approximately what proportion of all types of derivative transactions between financial institutions?
A credit portfolio manager analyzes a large retail credit portfolio. Which of the following factors will represent typical disadvantages of market-linked credit risk drivers?
I. Need to supply a large number of input parameters to the model
II. Slow computation speed due to higher simulation complexity
III. Non-linear nature of the model applicable to a specific type of credit portfolios
IV. Need to estimate a large number of unknown variable and use approximations
Most loans and deposits in the interbank market have a maturity of:
The potential failure of a manufacturer to honor a warranty might be called ____, whereas the potential failure of a borrower to fulfill its payment requirements, which include both the repayment of the amount borrowed, the principal and the contractual interest payments, would be called ___.
Which of the following risk types are historically associated with credit derivatives?
I. Documentation risk
II. Definition of credit events
III. Occurrence of credit events
IV. Enterprise risk
Foreign exchange rates are determined by various factors. Considering the drivers of exchange rates, which one of the following changes would most likely strengthen the value of the USD against other foreign currencies?
Which one of the following four models is typically used to grade the obligations of small- and medium-size enterprises?
In the United States, Which one of the following four options represents the largest component of securitized debt?
Which one of the following four options correctly identifies the core difference between bonds and loans?
Beta Insurance Company is only allowed to invest in investment grade bonds. To maximize the interest income, Beta Insurance Company should invest in bonds with which of the following ratings?
Which one of the following four statements correctly defines credit risk?
Which one of the following four statements regarding bank's exposure to credit and default risk is INCORRECT?
Which one of the following four parameters is NOT a required input in the Black-Scholes model to price a foreign exchange option?
Alpha Bank determined that Delta Industrial Machinery Corporation has 2% change of default on a one-year no-payment of USD $1 million, including interest and principal repayment. The bank charges 3% interest rate spread to firms in the machinery industry, and the risk-free interest rate is 6%. Alpha Bank receives both interest and principal payments once at the end the year. Delta can only default at the end of the year. If Delta defaults, the bank expects to lose 50% of its promised payment.
What may happen to the Delta's initial credit parameter and the value of its loan if the machinery industry experiences adverse structural changes?
A credit analyst wants to determine if her bank is taking too much credit risk. Which one of the following four strategies will typically provide the most convenient approach to quantify the credit risk exposure for the bank?
An asset manager for a large mutual fund is considering forward exchange positions traded in a clearinghouse system and needs to mitigate the risks created as a result of this operation. Which of the following risks will be created as a result of the forward exchange transaction?
According to the largest global poll of foreign exchange market participants, which one of the following four global financial institutions was the most active participant in the global foreign exchange market?
ThetaBank has extended substantial financing to two mortgage companies, which these mortgage lenders use to finance their own lending. Individually, each of the mortgage companies have an exposure at default (EAD) of $20 million, with a loss given default (LGD) of 100%, and a probability of default of 10%. ThetaBank's risk department predicts the joint probability of default at 5%. If the default risk of these mortgage companies were modeled as independent risks, the actual probability would be underestimated by:
All of the four following exotic options are path-independent options, EXCEPT:
From the bank's point of view, repricing the retail debt portfolio will introduce risks of fluctuations in:
I. Duration
II. Loss given default
III. Interest rates
IV. Bank spreads
Which one of the following four examples would not be considered a typical source of market risk?
In analyzing the historical performance of a financial product, you are concerned about "fat tails", the probability of extreme returns compared to realized returns. Which of the following measures should you use to determine if the product return distribution of the product has "fat tails"?
On January 1, 2010 the TED (treasury-euro dollar) spread was 0.9%, and on January 31, 2010 the TED spread is 0.4%. As a risk manager, how would you interpret this change?
Which one of the following four statements presents a challenge of using external loss databases in the operational risk framework?
After one year and spending USD 1.0 million, a bank finally succeeds in recovering USD 10 million on an exposure that, at the time of its default, was valued at USD 20 million. If the recovery discount rate is 10%, what is the estimate of the recovery rate?
Which one of the following four statements best describes challenges of delta-normal method of mapping options positions?
Delta-normal method understates
Which one of the following four statements about economic capital of a bank is correct?
Which of the following correctly identifies reasons for collecting internal operational risk event and loss information?
I. Assessing the risk of specific areas of concern.
II. Evaluating risk events and outcomes.
III. Collecting data for capital modeling.
IV. Getting insight into risk events in other firms in the industry.
Which one of the four following aspects of legal risk is NOT included in the Basel II Accord?
Which one of the following four statements about hedging is INCORRECT?
The market risk manager of SigmaBank is concerned with the value of the assets in the bank's trading book. Which one of the four following positions would most likely be not included in that book?
A risk analyst is considering how to reduce the bank's exposure to rising interest rates. Which of the following strategies will help her achieve this objective?
I. Reducing the average repricing time of its loans
II. Increasing the average repricing time of its deposits
III. Entering into interest rate swaps
IV. Improving earnings capacity and increasing intermediated funds
To ensure good risk management which of the following should be true about the CRO role and function?
Which one of the four following non-statistical risk measures are typically not used to quantify market risk?
A hedge fund trader buys options to establish an exposure in the currency market, thereby effectively removing the risk of being able to participate in a gapping market. In this case the options premium represents the price paid for eliminating the execution risk of
If the yield on the 3-month risk free bonds issued by the U.S government is 0.5%, and the 3-month LIBOR rate is 2.5%, what is the TED spread?
Which one of the four following statements about back testing the VaR models is correct?
Back testing requires
Which one of the four following statements about the Risk Adjusted Return on Capital (RAROC) is correct?
RAROC is the ratio of:
A bank customer can use either a plain vanilla option or an option contract with volumetric flexibility to reduce the following risks:
I. Market Risk
II. Basis Risk
III. Operational Risk
Which one of the following statements accurately describes market risk tolerance?
A bank considers issuing new capital to increase its Tier 1 capital levels. Which of the following financial instruments would most likely to be considered?
For a bank a 1-year VaR of USD 10 million at 95% confidence level means that:
According to Basel II what constitutes Tier 2 capital?
Normally, commercial banking can be viewed as a fixed income carry trade since
For two variables, which of the following is equal to the average product of the deviations from their respective means?
Which of the following statements depicts a difference between funding liquidity risks and trading liquidity risks?
A bank owns a portfolio of bonds whose composition is shown below.
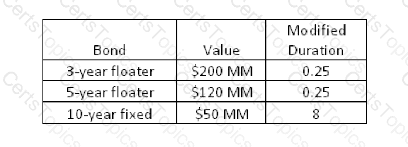
What is the modified duration of the portfolio?
The exercise for an American type option prior to expiration day is virtually certain in the following case:
Which one of the four following statements regarding minimum loss data standards is not correct?
Which of the following statements about implementation of a successful RCSA program is correct?
It is commonplace for the sellers of a single-name Credit Default Swap to post collateral to the buyer. What determines the amount of collateral posted?
In hedging transactions, derivatives typically have the following advantages over cash instruments:
I. Lower credit risk
II. Lower funding requirements
III. Lower dealing costs
IV. Lower capital charges
What is the role of market risk management function within a bank?
I. Control and minimize the risks the bank should take.
II. Establish a comprehensive market risk policy framework.
III. Define, approve and monitor risk limits.
IV. Perform stress tests and other qualitative risk assessments.
Since most consumers of natural gas do not have the ability to store it, they contract with gas suppliers to receive a flow of natural gas equal to a specific number of MMBT's per day (MMBT is millions of British Termal Units, the unit in which gas futures are quoted on the U.S. markets). To protect against price increases with a bank, the natural gas consumer, concerned with the average price over the course of the month, will use the following contracts:
Oliver McCarthy owns a portfolio of bonds. Which of the following choices equals the modified duration of Oliver's portfolio?
To reduce the variability of net interest income, Gamma Bank can swap positions that make its duration gap equal to
According to Basel II what constitutes Tier 1 capital?
Which among the following are shortfalls of the static liquidity ladder model?
I. The static model gives a liquidity estimate only after the bank faces the liquidity problem.
II. The static model can only make projections over a few days.
III. The static model does not incorporate uncertainty in the analysis.
The mark-to-market process includes which one of the following activities?
A trader for EtaBank wants to take a leveraged position in Collateralized Debt Obligations. If these CDOs can be used in a repo transaction at a 20% haircut, what is the maximum leverage factor for a transaction with the CDOs?
James Johnson bought a coupon bond yielding 4.7% for $1,000. Assuming that the price drops to $976 when yield increases to 4.71%, what is the PVBP of the bond.
John owns a bond portfolio worth $2 million with duration of 10. What positions must he take to hedge this portfolio against a small parallel shifts in the term structure.
What do option deltas measure?
Using the definitions used by JPMorgan Chase in their annual report, which of the following exposure types would be considered as a non-trading risk exposure?
I. Short term equity investments
II. Loans held to maturity
III. Mortgage servicing rights
IV. Derivatives used to manage asset/liability exposure.
Which of the following are the most common methods to increase liquidity in stressed conditions?
I. Selling or securitizing assets.
II. Obtaining additional credit lines.
III. Securing a better credit rating.
A bank has a Var estimate of $100 million. It is considering a new transaction which has a correlation of 0.35 with the current portfolio and a standalone VaR estimate of $5 million. What would be the new VaR for the bank if it carried out the transaction?
The operational risk policy should include:
I. The firm's definition of risk
II. The governance of operational risk including who owns it, what it owns, and how issues should be escalated
III. The main activities and elements that are managed by the operational risk function
For non-retail exposures, which one of the following factors must be determined by a bank when using the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach?
Why is economic capital across market, credit and operational risks simply added up to arrive at an estimate of aggregate economic capital in practice?
While contractually, depositors are not required to keep liquid funds on deposit for very long, in fact they tend to leave their deposits for longer periods of time, even if interest rates rise and the bank does not raise its deposit interest rate. What does a bank consider these deposits to be?
A risk associate is trying to determine the required risk-adjusted rate of return on a stock using the Capital Asset Pricing Model. Which of the following equations should she use to calculate the required return?
Which one of the following statements is an advantage of using implied volatility as an input when calculating VaR?
Why do regulatory standards impose formulaic capital calculations for all of the banks activities?
I. If the banks use different models it is difficult for a regulator to compare results across banks.
II. By imposing standardized calculations regulators can make sure that banks are not missing key risks in their calculations.
III. By imposing standardized calculations regulators can make sure that banks do not use capital calculations to game the banking regulation system.
Which of the following risk measures are based on the underlying assumption that interest rates across all maturities change by exactly the same amount?
I. Present value of a basis point.
II. Yield volatility.
III. Macaulay's duration.
IV. Modified duration.
BetaFin has decided to use the hybrid RCSA approach because it believes that it fits its operational framework. Which of the following could be reasons to use the hybrid RCSA method?
I. BetaFin has previously created series of RCSA workshops, and the results of these workshops can be used to design the questionnaires.
II. BetaFin believes that using the questionnaire approach should be more useful.
III. BetaFin had used the questionnaire approach successfully for certain businesses and the workshop approach for others.
IV. BetaFin had already implemented a sophisticated RCSA IT-system.