Refer to the following exhibit.
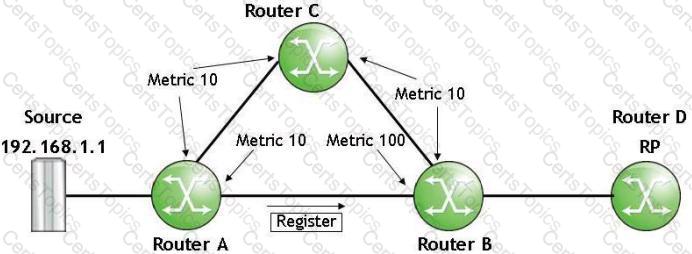
The interfaces' IGP metric is as shown and PIM is using unicast table for RPF-check. What will happen when Router B receives the register message on its interface facing Router A?
What is the destination address for MLDv2 report?
Which of the following is a reason why using unicast flows to send data to multiple receivers is not a scalable solution?
An IGMP version 3 receiver signals EXCLUDE mode with an empty EXCLUDE list. What does this indicate?
Which of the following statements is false regarding BSR and RP?
How does IGMP snooping eliminate multicast flooding on the LAN?
Which of the following ranges is reserved for IPv6 SSM multicast address?
Which of the following data delivery models are most applicable to multicast data delivery? (Choose two)
Four routers share a multi-access network. Router A is configured with a PIM DR priority of 10, Router B is configured with a PIM DR priority of 100, Router C and Router D are at the default value. Router D has the highest IP address. Which Router will be elected the PIM DR?
Which of the following is true regarding the IPv4 multicast address format?
Which protocol is used to establish the I-PMSI in Draft Rosen?
Which of the following is NOT a function of Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route?
Which of the following multicast packets can be forwarded in the Internet?
How many bits of the IPv4 multicast address directly match bits in the multicast MAC address?
Which of the following describes UMH (Upstream Multicast Hop) selection?
Which of the following services is provided by the use of PIM as a multicast routing protocol?
In Draft Rosen, a PE router encapsulates customer multicast packets into provider packets. What source IP address is used for the provider packets?
Which of the following fields is used in the PATH message to uniquely identify an S2L Sub-LSP?
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of multicast for delivering data to multiple receivers?
Which of the following about MLD snooping is FALSE?
What issues have to be resolved to support the deployment of SSM? (Choose two)
Who periodically sends IGMP Host Membership Queries?
Which of the following are NOT characteristics of the many to many model of multicast data delivery? (Choose two)
Refer to the following exhibit.
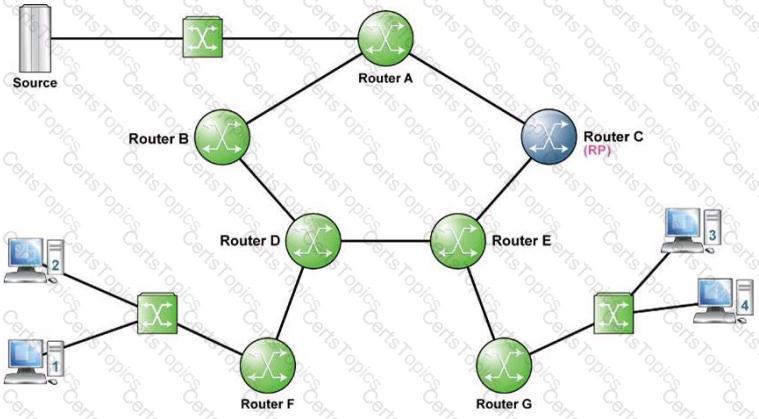
Assume all links have an equal metric in the IGP. Receiver 2 has joined the multicast group and the source is sending. After the switchover of Router F, will a branch of the Shared Path Tree still exist between Router D and Router E?
Which of the following PIM messages are sent via unicast? (Choose two)
How often will a router issue IGMP Host Membership Reports for group 224.0.0.2?
Which of the following is a name for PIM Sparse Mode operation that utilizes an RP?
Which of the following PIM messages are sent towards RP? (Choose two)
What is the Solicited-node multicast address for host 2001:1000:2000:3000::2001:2002:2003?
Which of the following statements about the PIM messages for IPv6 multicast routing is false?
Click the exhibit.
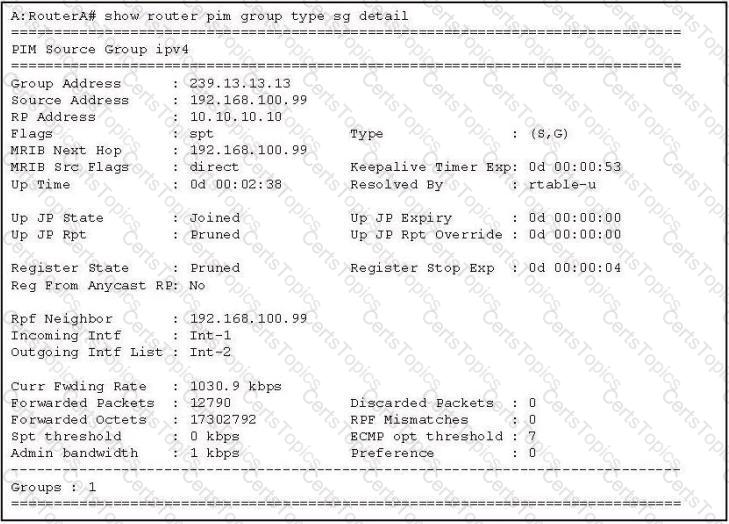
Which of the following describes the router that produced the output shown in the exhibit?
Which of the following describes how customer multicast routing information is distributed in NG MVPN?
An Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR is unable to locate a multicast source address in the multicast routing table. However, the source address is available in the unicast routing table. Which statement best describes the default RPF check behavior of the Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR?
An IGMP version 3 receiver signals INCLUDE mode report with an empty INCLUDE list. What does this indicate?
Which MAC address does the IPv4 multicast address 239.231.42.11 translate to?
Click the exhibit.

Which of the following BEST describes the multicast LAN?
Which of the following are NOT characteristics of the many-to-many model of multicast data delivery? (Choose two)