ZZ is a data security company that is responsible for cyber security m a large shopping mall 21 uses Network Configuration Management (NCM) to assist it in meeting the various needs of the mall's user community.
Which THREE of the following are advantages provided by NCM?
Rio owns an architects business which employs 12 skilled architects and four administrative staff.
The Office Manager has just attended a workshop on internal controls and the way in which they can improve organisations. He intends to implement some internal controls as soon as possible.
What are the limitations of an internal control system in Rio's business?
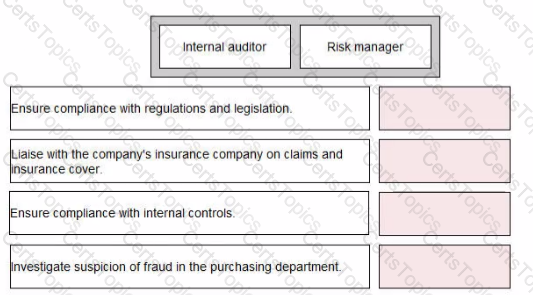
Assuming a company has both internal auditors and risk managers, indicate which of these would perform the duties listed below:
L is a specialist deep sea diving company The company specialises in challenging tasks that are often rejected by other companies as being too risky Most assignments are difficult and some are very dangerous L has very experienced divers who are highly trained and are safety conscious In spite of the dangerous work, L has an excellent success rate and is highly sought after L charges very high fees for its work Despite L's precautions, the likelihood of accidents is high and the consequences are also high L has an excellent insurance which has always been very expensive but the price has just been increased by 40%
Which of the following is correct?
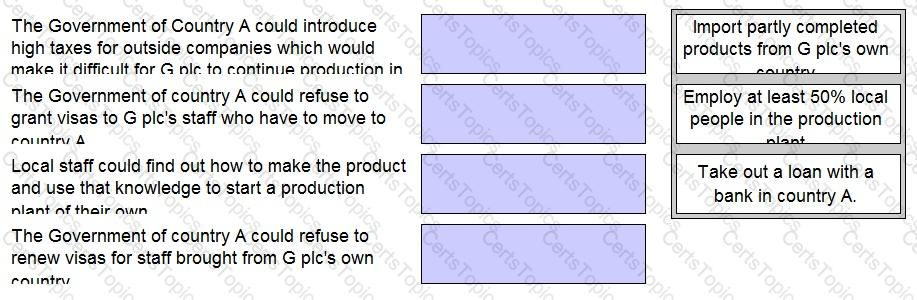
G plc has decided to move its production plant to overseas Country A. This would make the product cheaper to produce. The technology used to make the product is very advanced and some of the staff would have to move to Country A.
The Production Director has identified that there are some political risks in moving to Country A.
Match the methods of reducing the political risks associated with the move to Country A with the corresponding risks.
A large department store has just discovered that the staff in the store coffee shop have been defrauding the company for the past three years. The six employees who work in the coffee shop have been keeping a proportion of the cash takings, concealing the theft by not recording all sales up in the till They shared the proceeds of this fraud between them The fraud was only uncovered when one of the employees left and his replacement reported the theft to management rather than becoming involved in the crime
Which of the following best describes the role of the store's internal controls in the context of this fraud?
Which THREE of the following are principles of good corporate governance according to the UK Corporate Governance Code?
CH makes a popular type of chocolate bar The bars are made on a production line and are scanned for size and shape as they move along the line Wrong sized and misshapen bars are rejected as being poor quality. The scanner detects 90% of poor quality bars. If CH wants to reduce the risk of poor quality bars being sold to the public it can add a further check by a person scanning the production line as well. this check would detect 80% of poor quality bars
If the further check was implemented what percentage of poor quality bars would still get through the checking process?
Which of the following is an ethical dilemma?
Company N is considering opening another production plant in Northland, a country 2000 km from its current production plant location N would also sell its products in Northland
Which TWO of the following are business risks'
C is an accounts clerKwho is supposed to sign each invoice as evidence that she has conducted checks against supporting documents Sometimes C signs invoices without making these checks
D is a member of the internal audit team He has been told to conduct compliance tests on whether C is checking the invoices property
Which of the following would grve D a false sense of assurance that C's checks have been in operation?
Select ALL that appry
The Head of IT Security has been asked to conduct a detailed forensic analysis of a suspected data breach that ted to customer credit card details being intercepted.
Which TWO of the following would be suitable objectives for such a forensic analysis?
The treasurer of IOK is considering entering into a money market hedge in order to hedge a payable.
Which of the following might be valid explanations for the use of a money market hedge for this purpose?
MNB is a multinational IT company with headquarters in Asia and with operations in all continents.
MNB is attempting to expand its operations in Europe. This is seen as a major challenge as the European market is very well developed and highly competitive.
MNB develops and manufactures its own products. Parts and assemblies are sourced across Asia, America and Europe. These are sometimes purchased locally as a condition of a contract, but MNB aims to include as much of its own equipment as possible. Transfer prices between MNB's subsidiaries can be set in YEN, USD, EURO, GBP. Transfer prices are revised every month in line with production times as most goods are made on short order with sales cycles running at 3-4 months.
What types of risk are being presented here?
J plc is a wholesale building supply business. It has a large warehouse where some of its materials are stored. Last month three accidents occurred where employees were slightly injured whilst moving items from the 5th shelf. The 5th shelf is located 15 metres up from the ground.
This is a health and safety risk and could also be a reputation risk in the longer term.
Which of the following risk mitigations should the company employ?
SC is a professional football club which is currently listed on a recognised stock exchange. There is a proposal that it builds a new stadium at a location a considerable distance from its current stadium.
There is strong support within the club for the move as the current ground is now over 40 years old and has not been extensively modernised in that time.
However, there is a lot of opposition to the move in the area where it is proposed to locate the new stadium. Objectors claim that the new stadium will increase traffic and pollution in the area and will adversely affect the value of their properties.
Which of the following statements about the responsibility of the board of SC is correct?
The managers of a company are agents for the shareholders tasked with increasing shareholders' wealth. Which of the following will usually increase shareholders' wealth?
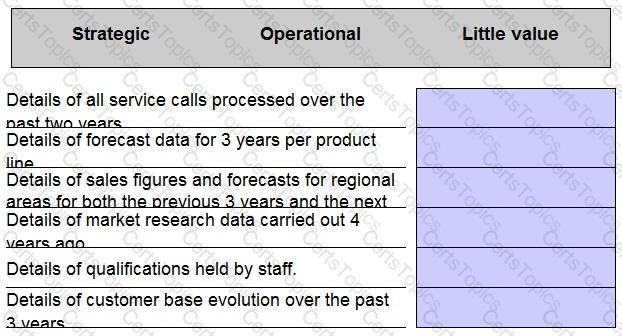
H sells machinery and also associated services, such as advice and repairs. H's industry is going through considerable transformation.
Classify each of the examples of information available to H's management as strategic, operational or of having little value.
NLC, a retail chain, is considering moving its information systems which support its point of sale infrastructure into the cloud.
Which TWO factors should it consider in choosing its supplier?
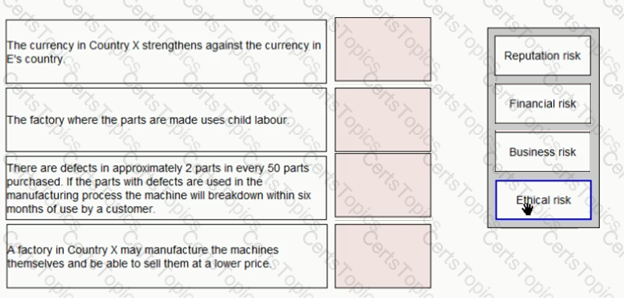
TT is a jewellery manufacturer in country A It makes jewellery from precious metals and stones and sells it to shops in country A and also overseas It is the 3rd largest company in country A with a huge turnover
TT has found it very difficult to prevent staff committing fraud and last year the Board was sure that the year end inventory was lower than it should have been Gross profit was also slightly lower than expected
Which TWO of the following internal controls would be most effective in helping to reduce staff fraud within TT?
JKL makes large export sales to customers in country X, whose currency fluctuates significantly against JKL's home currency JKL also makes large purchases from suppliers in countrrOC All of these transactions are in country X's currency
JKL's treasurer does not actively hedge currency risks because there is a natural hedge in place due to the company making both sales and purchases in the same currency
JKL's board has instructed the treasurer to put active hedging measures in place because the risk report would otherwise have to disclose the fact that JKL has a currency risk which is not actively hedged
Which of the following statements are correct? Select ALL that apply.
D plc is a public relations company. Shares in D plc have recently been listed on the UK stock exchange.
D plc has an internal audit department that reports to the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). The CEO is considering outsourcing internal audit to an audit firm, which would not be the firm that conducts D plc's external audit.
Identify THREE advantages to D plc of outsourcing internal audit in this way.
Will owns $400,000 of shares in Company X.
Company X has a daily volatility of 1% of its share price.
Calculate the 28 day value at risk that shows the most Will can expect to lose during a 28 day period.
(Will wishes to be 90% certain that the actual loss in any month will be less than your predicted figure).
Give your answer to the nearest $000.
Which of the following are objectives of the audit planning procedure?
Multinational companies have a variety of methods by which to manage currency risk.
Select ALL internal hedging methods from the following list.
In-depth analysis showing the identification and quantification of exposure to financial risk has become more accessible in recent years. Several varieties of analysis are now available.
Which of the following statements are true?
Which method of quantifying risk exposure can be used to calculate the maximum loss on a portfolio occurring within a period of time with a given probability?
Company H operates a fleet of lorries. The Internal Auditor recently conducted an investigation into the transport needs of the company. Their report recommended that the lorries be disposed of, the drivers made redundant, and the distribution of the company's products be outsourced.
The type of investigation carried out by the Internal Auditor is best described as a:
A UK based company is considering an investment of GB£1,000,000 in a project in the USA. It is anticipated that the following cash flows will arise from this project.
The cash flows will be either US$400,000 with a probability of 40% or US$700,000 with a probability of 60% for each of the next three years; remitted to the UK at the end of each year.
Currently GB£1.00 is worth US$1.30.
The expected inflation rates in the two countries over the next four years are 2% in the UK and 4% in the US.
Applying the Purchasing Power Parity Theory, which of the following represents the expected net present value of the project in GP£ (to the nearest whole pound)?
E purchases parts for one of the machines it manufactures from Country X Place the risk classification next to the risk it relates to:
Which of the following is the major advantage of Cloud storage for an enterprise?
There are many method for appraising capital projects.
Select ALL correct statements.
B is a small retail bank that offers customers many on-the services B is keen to ensure sound security both to protect the bank's assets and also to safeguard customer privacy
B's IT Security Manager has suggested that the bank should use two phase authentication for access to the on-line systems
Which TWO of the following are examples of two phase authentication?
GUJ A small but rapidly expanding company has recently opened several branches in locations far away from the Head Office. All of the branches are relatively small with no one branch accounting for more than 5% of turnover. Management has decided that the company is not yet large enough to install an Internal Audit function but is, nonetheless, concerned about maintaining adequate control and monitoring at the branches whilst allowing Branch Managers the opportunity to react to local circumstances as appropriate.
Which of the following measures would assist Head Office management in maintaining appropriate monitoring and control at the branches?
N, a large company in the food production industry, has grown over the years by the acquisition of several smaller rivals. The company has ten branches located in its home country and has just opened a foreign branch for the first time. It has recently made some changes to the structure and implementation of its control system.
Which TWO of these would be most likely to improve the overall control system?
GHY is a listed company. Tom is GHY's CEO and Peter is its non-executive Chair of the Board. Tom and Peter both have substantial relevant business and industrial experience and both are believed to have considerable integrity. Tom and Peter quickly developed a good working relationship after Peter's appointment. They have become close friends.
Tom briefs Peter on every aspect of the business. Tom and Peter jointly agree the agenda for every board meeting and both agree on the manner in which matters will be presented to the board.
Taking account of the principles of good corporate governance, which of the following statements is correct?
DFG is the largest bridge-building company in its home country, H. DFG works exclusively for the government of country H and the government awards DFG 80% of the contracts to build new bridges.
DFG's directors are considering using the big data approach to identify opportunities to increase sales revenues and profit.
Which of the following statements are true?
HBN is a service company that offers cloud-based data storage and management on behalf of clients HBN pays an independent accountancy firm to review its cybersecurity arrangements, conduct penetration tests and report to HBN's Board on the results
Which TWO of the following are correct?
DBB is a mining company. The company's business requires manners to work underground in hazardous conditions DBB takes every possible precaution to protect the safety and wellbeing of its miners, but that does not prevent the occurrence of four or five serious injuries every year. That number is small in relation to the many thousands of owners employed by DBB.
DBB's Board is preparing a risk map Most directors believe that injuries to miners should be classified as high Likelihood and high impact, which Is a category of risk that should be avoided according to the TARA framework One of the directors has suggested that the risk should be classified as low likelihood and high impact because that would move the risk into the quadrant associated with transference or sharing and so could be draft with by, say, insurance
Which TWO of the following are correct?
RFD, a listed company, is considering making an investment in a risky new venture. RFD has a substantial cash surplus that will be used to acquire the necessary resources. It is unlikely that RFD would have been able to raise finance for this investment because the company is already highly geared.
Which of the following statements about stakeholders' conflicting interests are true?
The managers of a company are agents for the shareholders tasked with increasing shareholders' wealth. Which of the following will usually increase shareholders' wealth?
You are the Management Accountant for P, a food manufacturing company with an annual sales revenue of $5 million.
You discover that the Production Manager's records are inconsistent. Raw materials purchased do not agree to the total recorded for transfers to production plus wastage. There is an average shortfall of 2% of purchases.
You investigated and discovered that there are often mistakes made during manufacturing that results in food that is safe to eat, but cannot be sold because of visual flaws. The Production Manager is supposed to scrap all such damaged product and write all such losses off as waste, but you discovered that he has been giving the damaged food to a charity that assists homeless people. No records are made of such gifts in order to conceal the losses due to manufacturing errors.
What should you do?
Which of the following is an ethical dilemma?
YHJ is considering an investment in a project that will cost $20 million. Annual fixed costs will be $12 million per year, excluding depreciation. Annual sales are forecast at 5 million units, with a contribution per unit of $8. After five years the equipment will be worn out and YHJ will have to spend $50 million on disposal costs. The discount rate is 10%.
Calculate the sensitivity of the net present value of this project to a 20% increase in the disposal costs.
YGH has recently completed a post completion audit on a five year contract that has only recently come to a conclusion. The main finding was that the project delivered most of the expected benefits, but that it cost significantly more to implement than had been anticipated at the project appraisal stage. YGH would not have proceeded if the true cost had been known at that stage.
The project was the responsibility of the production department, which is presently managed by G.
When the project was proposed, the production department was managed by H. H is now YGH's Director of Operations.
How should the finding from this post completion audit be interpreted?
Zia is an accountant and wishes to take out a Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) as a hedging instrument. The company treasurer has advised that a short-term interest rate (STIR) future would be better.
Which of the following is true of an STIR?
J is a manager in charge of a section in GDD's Buying department. J has eight staff who report to her. Including M, who has worked for GDD for seven months.
One afternoon, while J was absent on sick leave, M was asked to place an urgent order for plastic pellets that are vital for GDD's production process. The usual supplier could not supply the pellets on time to avoid a shortage and so M telephoned a new supplier and placed an order. When the supplier invoiced for the delivery, GDD's Accounts Payable Department rejected the invoice because the supplier did not have a valid account.
On investigation, it was revealed that M did not have the authority to place an order with a new supplier. Only J can authorise new accounts. M claimed that he had been unaware of the need to seek approval because he had never found it necessary to place an order with a new supplier before
Which TWO of the following statements ate correct?
ABC is a large supermarket chain which also has online shopping and home deliveries It has a 24/7 service which runs on a central server allowing all customers to enter new orders at any time This is a business critical service which, if not available, may lead to customers turning to alternative supermarket chains offering similar services, resulting in immediate turnover loss and possible long term customer loss.
ABC is contemplating the implementation of a hot standby facility, not only to cover for emergency disaster recovery, but also to allow for business continuity, allowing necessary maintenance and updates without service interruption.
Which of the following cybersecurity objectives is ABC concerned about in this scenario?
SDF has a variable rate loan of $100 million on which it is paying interest of LIBOR + 2%.
SDF entered into a swap with CV bank to convert this to a fixed rate 7% loan. CV bank charges an annual commission of 0.3% for making this arrangement.
Calculate the net payment from SDF to CV bank at the end of the first year if LIBOR was 3% throughout the year.
Give your answer in $ million, to one decimal place.
Match the descriptions shown in the boxes below with the method of quantifying risk exposure it best describes.
