Fortinet Related Exams
FCSS_NST_SE-7.6 Exam







Refer to the exhibit, which shows the partial output of command diagnose debug rating.
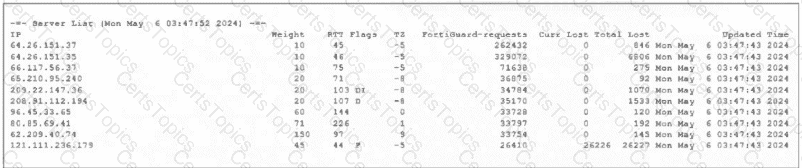
In this exhibit, which FDS server will the FortiGate algorithm choose?
Refer to the exhibit.
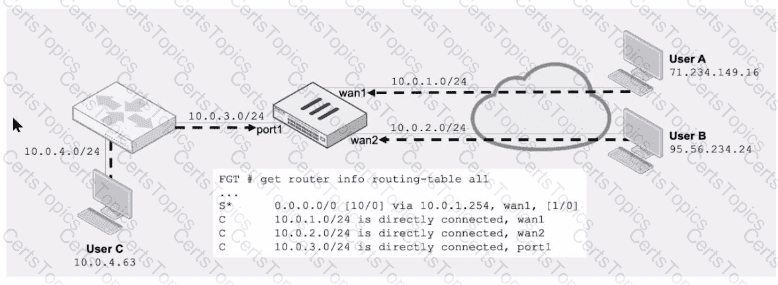
Assuming a default configuration, which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of a BGP debug command.
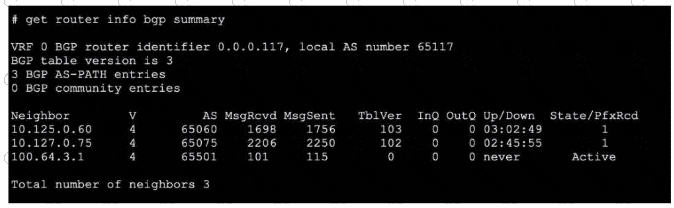
What can you conclude about the router in this scenario?