Snowflake Related Exams
ARA-C01 Exam







A Snowflake Architect created a new data share and would like to verify that only specific records in secure views are visible within the data share by the consumers.
What is the recommended way to validate data accessibility by the consumers?
A company has a Snowflake environment running in AWS us-west-2 (Oregon). The company needs to share data privately with a customer who is running their Snowflake environment in Azure East US 2 (Virginia).
What is the recommended sequence of operations that must be followed to meet this requirement?
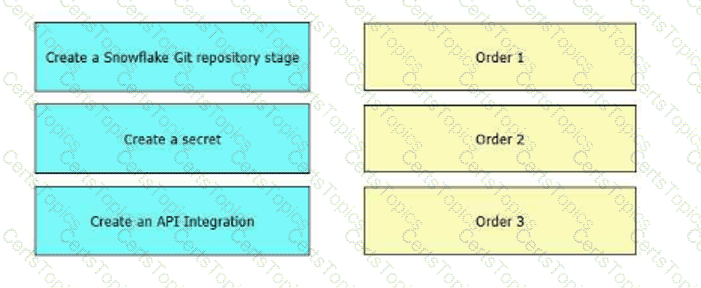
An Architect wants to integrate Snowflake with a Git repository that requires authentication. What is the correct sequence of steps to be followed?