A nulliparous woman at term presents with leaking fluid. Rupture of membranes confirmed. After 6 hours she is completely dilated, +2 station, has been pushing 2 hours with oxytocin at 10 mU/min. The fetal tracing is shown. What is the next step in management?
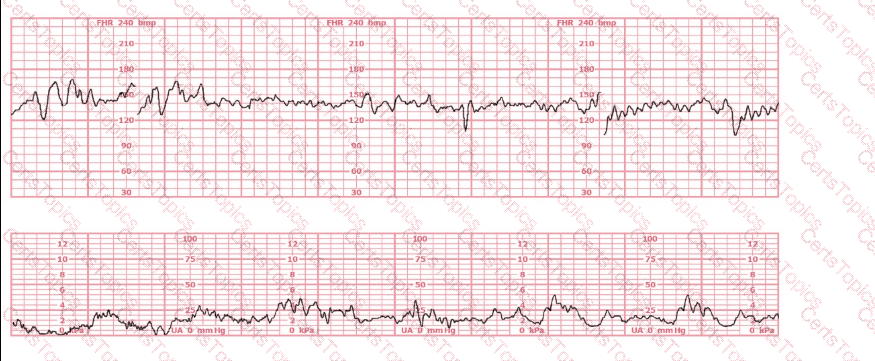
This fetal heart rate tracing is of a woman in labor with dichorionic-diamniotic twins at 36-weeks gestation, 4 cm dilated. She is on oxygen via face mask. Based on the fetal heart rate tracing, what is the most appropriate action?
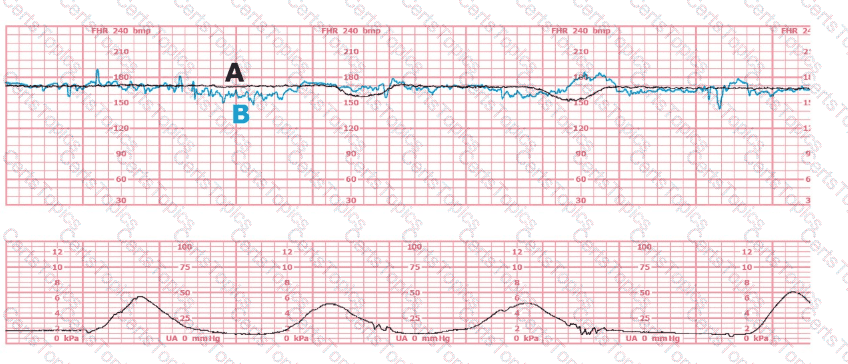
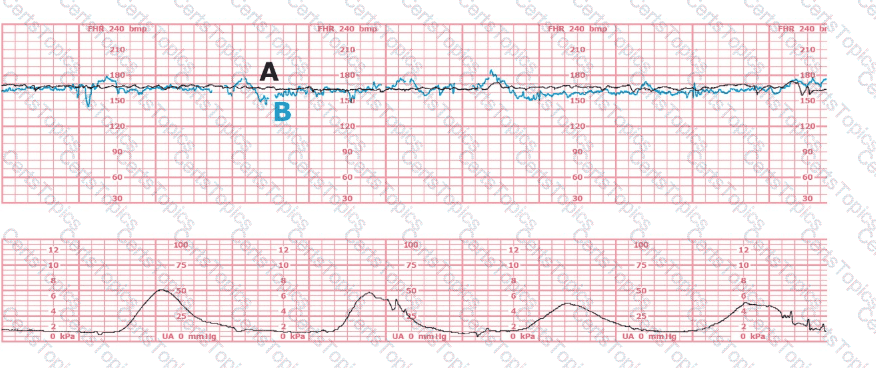
(Tracing A = black; Tracing B = blue)
A woman experiences an eclamptic seizure during the second stage of labor. An anticipated fetal heart rate abnormality post-seizure would be:
Stimulation of the vagus nerve in a healthy fetus will cause:
When accelerations precede a variable deceleration pattern, this is caused by
In the event of recurrent variable decelerations with thick meconium, amnioinfusion is recommended to:
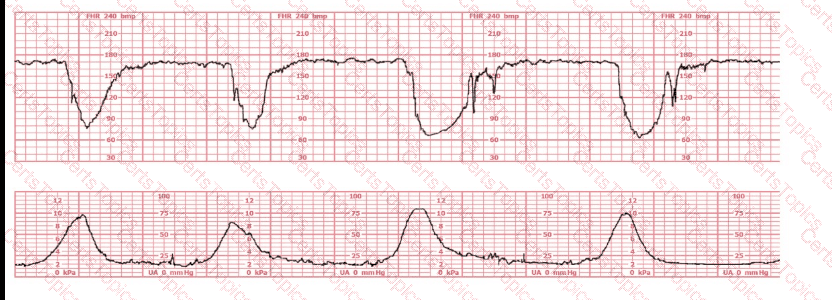
The decelerations seen in the fetal monitoring tracing shown are best described as:
(Full question)
Spontaneous fetal heart rate accelerations indicate
Maternal–fetal exchange during labor is diminished by:
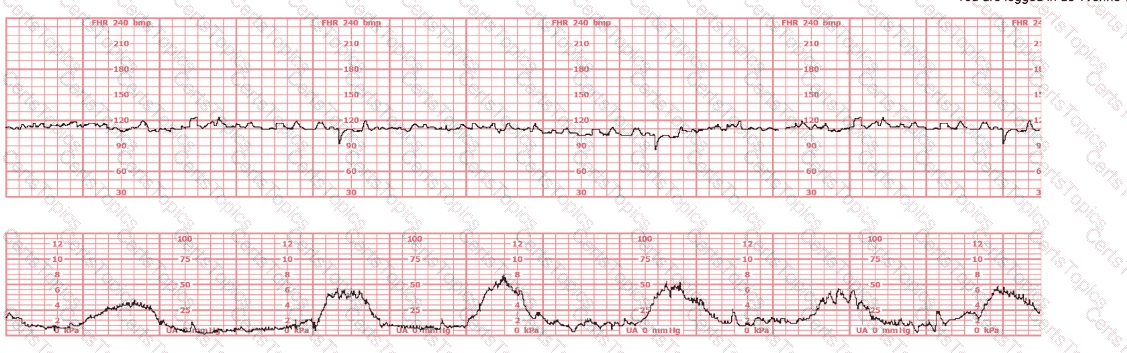
A woman is admitted to labor and delivery with vaginal bleeding. This tracing is obtained. This is most consistent with:
(Full question statement)
The fetal heart rate tracing shown is obtained upon the woman's admission to labor and delivery. This tracing is most consistent with what maternal condition?
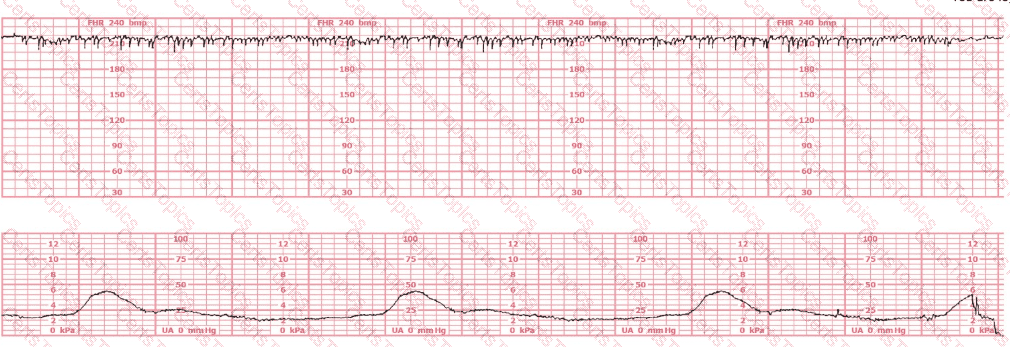
A fetal heart rate pattern shows no accelerations or decelerations. It would be interpreted as a Category II pattern if it occurred with:
Maternal fever can cause fetal tachycardia because the increased maternal temperature:
Sustained fetal supraventricular tachycardia that goes untreated is most likely to result in:
The ratio of oxyhemoglobin to the total amount of hemoglobin available is called oxygen
The factor that differentiates a prolonged deceleration from bradycardia is:
A woman in labor has been pushing for 4 hours. For the last 2 hours, there have been recurrent variable decelerations. Variability has evolved from moderate to minimal. Cervical exam is 10/100%/+2, fetal head OP. There has been no fetal descent for the last 45 minutes. Based on the tracing shown, the most reasonable approach is
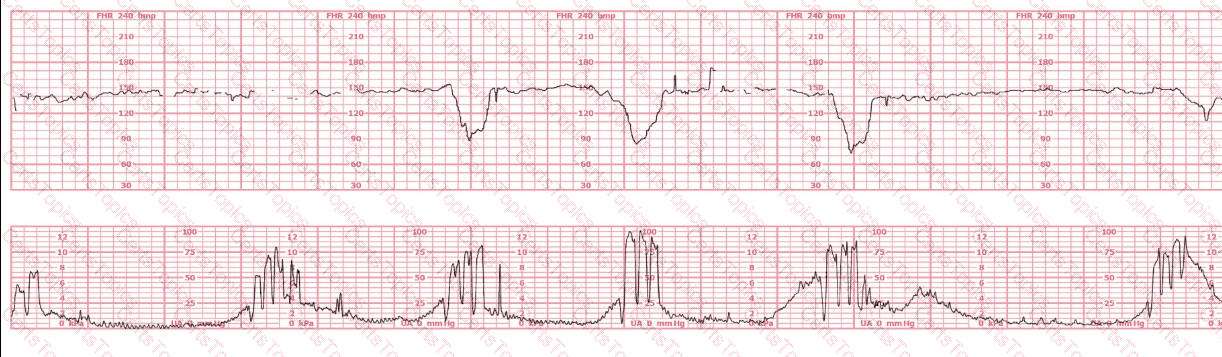
Based on the fetal heart rate tracing shown, the expected fetal pH would be:
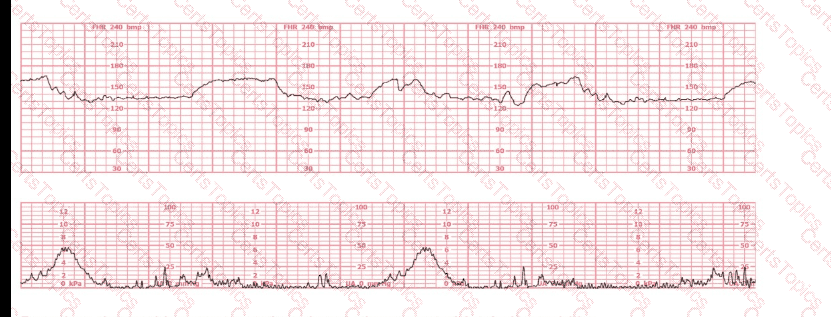
Interventions to decrease uterine activity should take place:
When the fetal heart rate is measured by a Doppler transducer and the intervals between heart beats are persistently identical, this shows as
The fetal heart rate tracing shown is consistent with
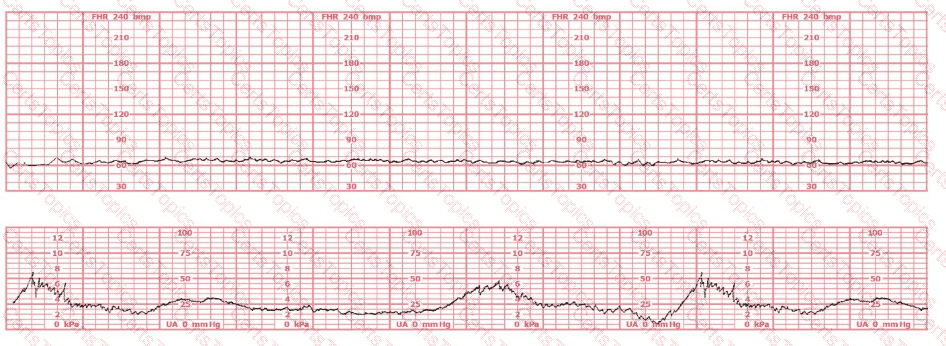
The black pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby A. The blue pattern represents the heart rate pattern for Baby B. A possible etiology of the baseline fetal heart rate of Baby A is:
A woman at 38-weeks gestation is admitted to labor and delivery following a fall down the stairs three hours ago. She started feeling contractions in the ambulance. The fetal heart rate tracing shown is on initial evaluation and represents 25 minutes. This tracing is most consistent with a
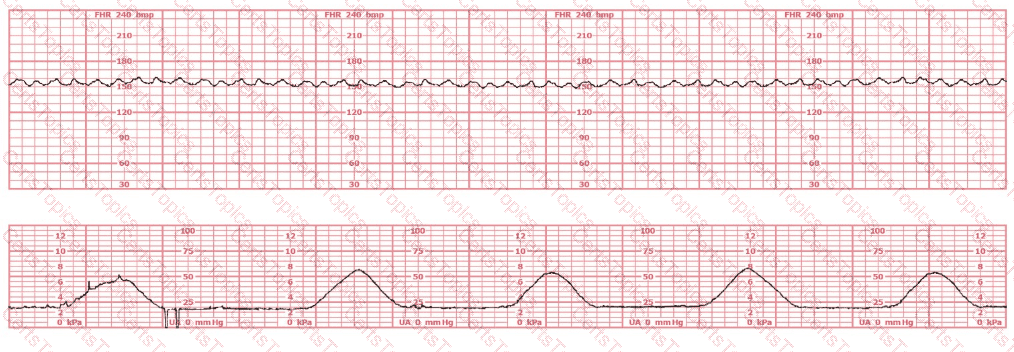
In documenting auscultation of the fetal heart rate, it is important to record findings in relationship to:
Based on the tracing shown, the first action should be to

A woman at 36-weeks gestation comes in because of uterine contractions radiating to the back. She has no insurance. In accordance with the Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA), she is obligated to be:
The tracing shown is a:
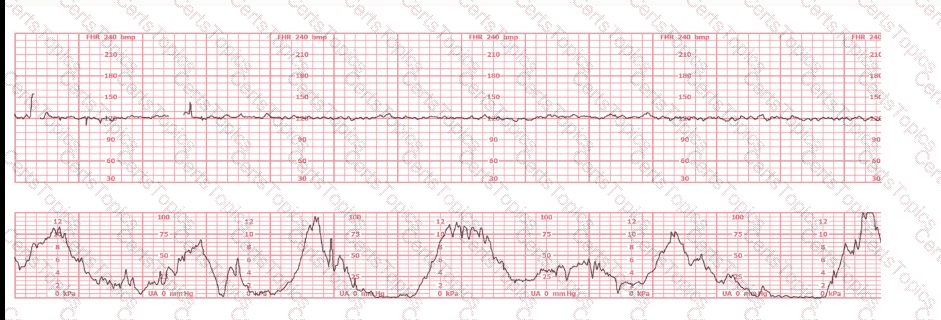
This tracing demonstrates:
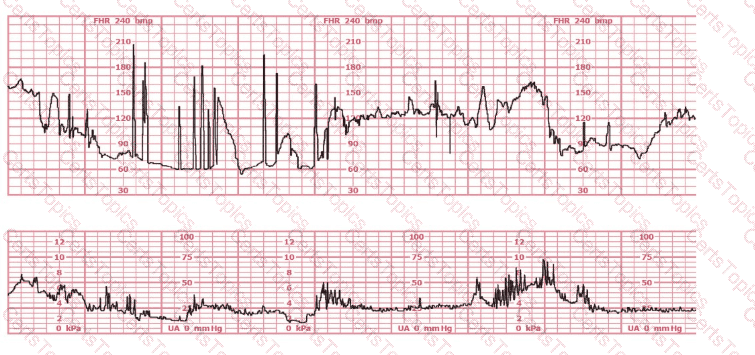
The tracing shown is a:
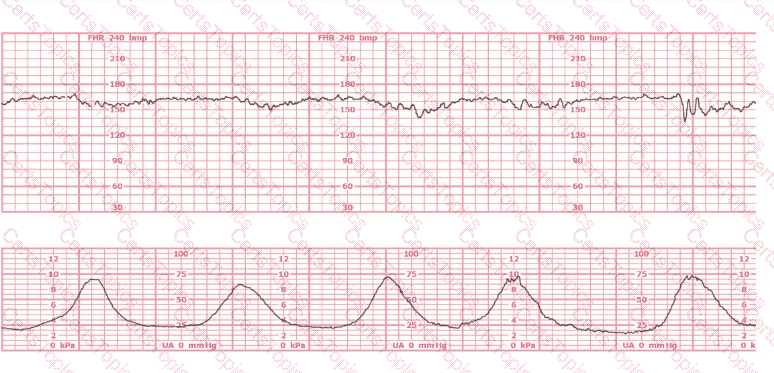
(Full question)
This tracing would be categorized as a
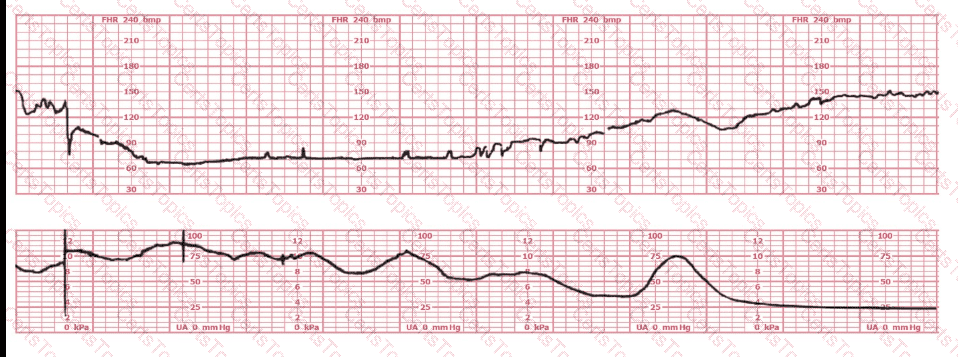
A woman is admitted at 41-weeks gestation for fetal evaluation following a motor vehicle accident. She reports that she hit her abdomen on the steering wheel. The underlying physiology of the tracing is most likely:
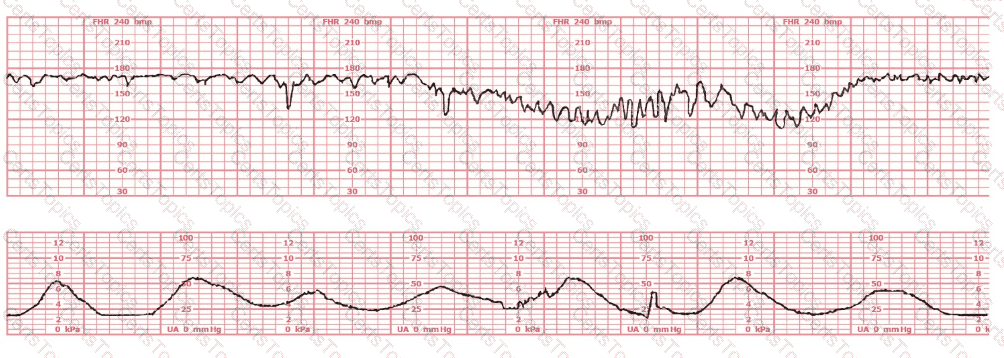
When auscultating the fetal heart rate, the Doppler should be placed over the fetal:
(Full question statement)
A dysrhythmia is noted. The pregnancy and labor course has been normal with no complications. The next step in management is to
A 30-year-old woman (G2P0) is experiencing preterm labor at 26-weeks gestation. She is receiving magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Her external fetal monitoring tracing over the past 30 minutes is shown. The next step would be to:
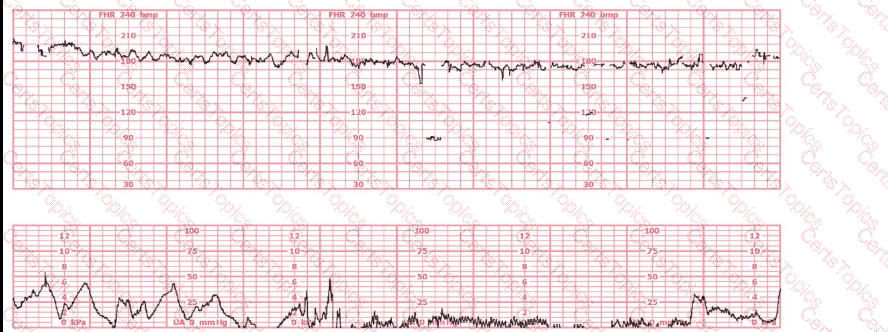
This tracing reflects:
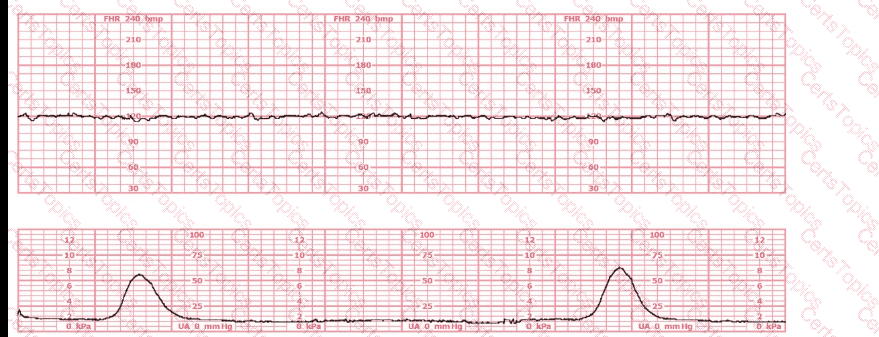
A sentinel or reportable event as defined by the Joint Commission or other regulatory bodies/agencies is one that
(Full question)
Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is a useful intervention which can