Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Assessment of likely fetal acid–base status is grounded in NCC-aligned principles that correlate fetal pH with fetal heart rate patterns, especially variability, presence/absence of accelerations, and type and depth of decelerations.
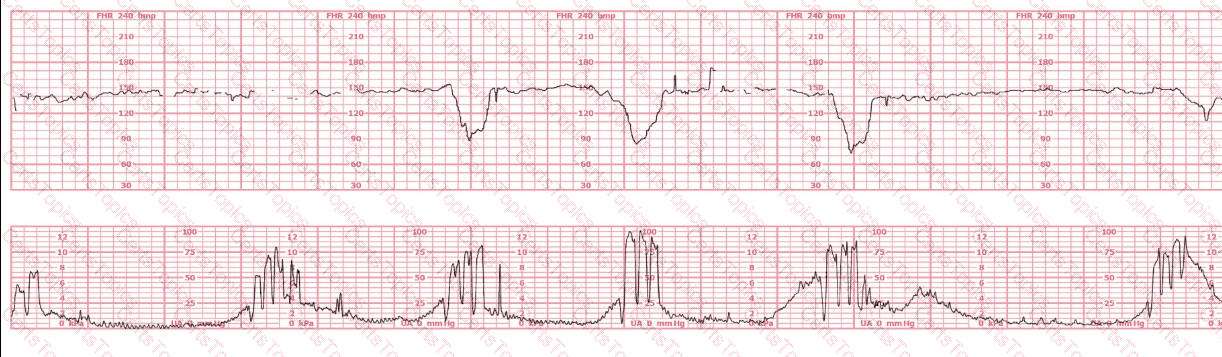
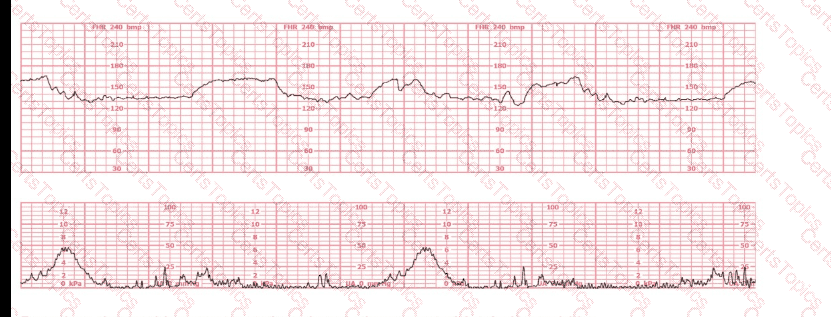
This tracing shows the following features:
Baseline:
The fetal heart rate baseline is approximately 140–150 bpm, within the normal 110–160 bpm range.
Variability:
Moderate variability is present—approximately 6–25 bpm amplitude.
Per NCC and NICHD definitions, moderate variability is strongly associated with normal fetal oxygenation and normal fetal pH > 7.20–7.25.
Accelerations:
There are occasional small accelerations, another strong indicator of normal fetal acid–base status.
Decelerations:
The tracing shows occasional variable decelerations, shallow and brief, recovering rapidly, typical of intermittent cord compression.
NCC references emphasize that intermittent, non-recurrent variables with moderate variability do not correlate with acidemia.
Uterine activity:
Contractions are present but not excessive, and fetal response remains reassuring.
Correlating tracing features with fetal pH (per NCC, AWHONN, Simpson, Menihan):
Moderate variability is the strongest intrapartum indicator of normal fetal pH.
The NICHD/NCC consensus repeatedly states that:
“The presence of moderate variability reliably predicts adequate fetal oxygenation and a fetal pH above the threshold associated with metabolic acidemia.”
Fetal pH below 7.15 is associated with:
Absent variability
Recurrent late decelerations
Recurrent deep variable decelerations
Prolonged bradycardia
None are present in this tracing.
Because the tracing demonstrates moderate variability, intermittent uncomplicated variables, and no recurrent late decelerations, the physiologic expectation is that the fetal pH remains normal, significantly above 7.15.
Therefore, the correct answer is: A (above 7.15).
[References:, NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide (2025); NCC Content Outline; NICHD Interpretation System; AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices; Miller’s Fetal Monitoring Pocket Guide; Menihan Electronic Fetal Monitoring; Simpson & Creehan Perinatal Nursing; Creasy & Resnik Maternal–Fetal Medicine., , ]