Identify which are key data used to transform information for a product value study:
Flow diagrams, latest cost estimate, labor reports, drawings, site plan, regulatory requirements
Customer requirements, overhead cost, competitive analysis, sample components, packaging requirements, warranty information
Design objectives, original cost estimate, drawings, specifications, resource models, customer demographics
Customer demographics, overhead cost, drawings, competitive analysis, sample components, labor reports
The Information Phase of the Value Methodology (VM) Job Plan involves gathering and transforming data to understand the subject of the study, as taught in the VMF 1 course (Core Competency #3: Value Methodology Job Plan). According to SAVE International’s Value Methodology Standard, “key data for a product value study typically includes design objectives, cost estimates, drawings, specifications, and resource models, which are transformed to define functions, costs, and constraints.” These data types are essential for a product-focused study (as opposed to a process or construction project), enabling the VM team to:
Understand the product’s purpose (design objectives).
Analyze costs (original cost estimate, before optimization).
Review technical details (drawings, specifications).
Assess resource use (resource models).Customer demographics may provide context but are not core to transforming information for a product value study.
Option A (Flow diagrams, latest cost estimate, labor reports, drawings, site plan, regulatory requirements): This is more suited for a process or construction project (e.g., flow diagrams, site plan), not a product value study.
Option B (Customer requirements, overhead cost, competitive analysis, sample components, packaging requirements, warranty information): While customer requirements and sample components are relevant, competitive analysis, packaging, and warranty are secondary; overhead cost is too specific and not a core data type for transformation.
Option C (Design objectives, original cost estimate, drawings, specifications, resource models, customer demographics): This is correct, as it includes the core data types for a product value study (design objectives, cost estimate, drawings, specifications, resource models), though customer demographics are less critical but acceptable as context.
Option D (Customer demographics, overhead cost, drawings, competitive analysis, sample components, labor reports): This includes less relevant data (customer demographics, competitive analysis, labor reports) and misses key items like design objectives and specifications.
Option C (Design objectives, original cost estimate, drawings, specifications, resource models, customer demographics) is correct, as it best aligns with the key data needed for a product value study.
An unwanted function of a hammer would be:
Swing arm
Apply force
Deliver force
Transmit vibration
Function Analysis in Value Methodology involves identifying and classifying functions of a product, process, or system using verb-noun combinations, as taught in the VMF 1 course (Core Competency #2). Functions are categorized as basic (essential to the purpose), secondary (supporting), or unwanted (undesirable outcomes). For a hammer, the basic function is to “deliver force” to drive a nail, while secondary functions like “swing arm” or “apply force” support this purpose. An unwanted function is an unintended or negative outcome of the hammer’s use.
Option A (Swing arm) is a supporting function, describing the action of the user’s arm to generate momentum, and is not unwanted.
Option B (Apply force) is a secondary function, as it describes the action leading to delivering force, and is not unwanted.
Option C (Deliver force) is the basic function of a hammer, essential to its purpose, and not unwanted.
Option D (Transmit vibration) is correct because it represents an unintended and undesirable outcome—vibration transmitted to the user’s hand can cause discomfort or fatigue, making it an unwanted function.
The VMF 1 course emphasizes identifying unwanted functions to target areas for value improvement, such as redesigning the hammer to reduce vibration.
Which type of value is the sum of labor, material, and other resources required to produce the subject?
Esteem Value
Exchange Value
Use Value
Cost Value
In Value Methodology, value is defined as the relationship between function and cost (value = function/cost), and different types of value are analyzed to assess worth, as taught in the VMF 1 course (Core Competency #4: Cost Analysis). According to SAVE International’s Value Methodology Standard, the types of value include:
Cost Value: “The sum of labor, material, overhead, and other resources required to produce the subject.” It represents the actual cost to create or deliver the product or system.
Use Value: The value of the functions the subject performs (e.g., what it does for the user).
Esteem Value: The value associated with prestige, aesthetics, or desirability (e.g., brand value).
Exchange Value: The value of the subject in terms of what it can be exchanged for (e.g., market value).
The question asks for the type of value that is the sum of labor, material, and other resources, which directly matches the definition ofCost Value. For example, the cost value of a car includes the costs of its parts, labor to assemble it, and overhead expenses.
Option A (Esteem Value) is incorrect because esteem value relates to subjective desirability, not production costs.
Option B (Exchange Value) is incorrect because exchange value is the market value, not the cost to produce.
Option C (Use Value) is incorrect because use value reflects the functional utility, not the resource costs.
Option D (Cost Value) is correct, as it is defined as the sum of resources required to produce the subject.
Which of the following letters represents the scope lines?
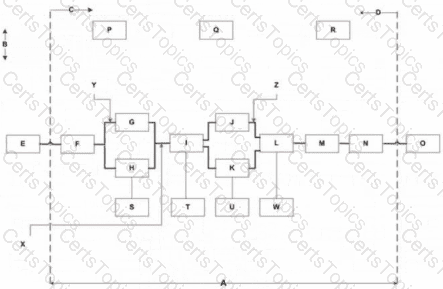
A
B
C
D
The diagram provided is a Function Analysis System Technique (FAST) diagram, a key tool in Value Methodology’s Function Analysis phase, as taught in the VMF 1 course (Core Competency #2). FAST diagrams map the relationships between functions of a system, with the horizontal axis showing the “how-why” logic (critical path) and the vertical axis showing supporting functions. The vertical demarcations on the left and right of a FAST diagram are calledscope lines, which define the boundaries of the study. According to SAVE International’s Value Methodology Standard, “scope lines indicate the limits of the system or project being analyzed, separating the functions within the study’s scope from external functions or assumptions.” This was previously established in Question 15, where scope lines were identified as the correct term for these vertical demarcations.
In the FAST diagram:
The dashed vertical lines on the left and right are labeledB(left) andD(right). These lines define the scope of the study, with functions inside the lines (e.g., E, F, G, J, L, M, N, O) being within the study’s focus, while functions outside (e.g., P, Q, R) are external assumptions or higher-level objectives.
Ais a horizontal line at the bottom, representing the boundary of the diagram but not the scope lines.
Cis an arrow indicating the direction of the “why” axis (left), not a scope line.
Since the question asks for the letter that “represents the scope lines,” and both B and D are scope lines, the correct answer must be one of these. However, the options only allow for one letter to be selected, and in FAST diagramming convention, the left scope line (B) is often emphasized as the primary boundary for defining the study’s starting point (e.g., the higher-order function E, as identified in Question 18). Thus,Bis the most appropriate choice among the options provided.
Option A (A) is incorrect because A is a horizontal line, not a vertical scope line.
Option B (B) is correct, as B is the left vertical scope line, marking the boundary of the study’s scope.
Option C (C) is incorrect because C is an arrow, not a scope line.
Option D (D) is also a scope line (the right boundary), but since only one letter can be selected and B is the left scope line (often the primary focus in FAST diagramming), B is chosen. If the question intended to allow both B and D, the phrasing would need adjustment.
Copyright © 2021-2026 CertsTopics. All Rights Reserved

