UiPath Related Exams
UiPath-ADAv1 Exam







A project built using REFramework pulls phone numbers from a database of employees and creates queue items for each one. Following processing, these elements must be added to a financing
application. The queue item holding a phone number becomes invalid if a digit is accidentally left out because of a human mistake. As a requirement, queue items that contain partial numbers should not be accepted.
What type of error should be thrown according to best practices?
A developer has designed an automation workflow which comprises:
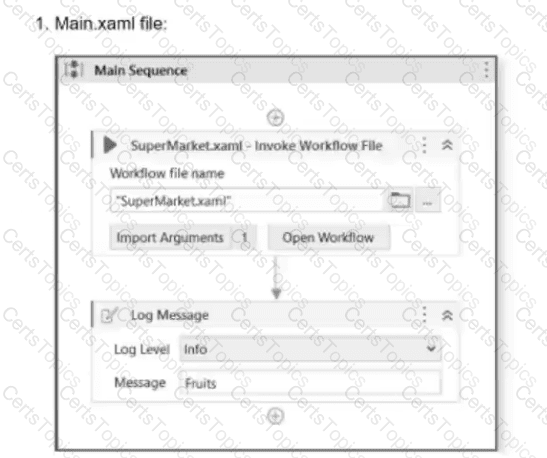
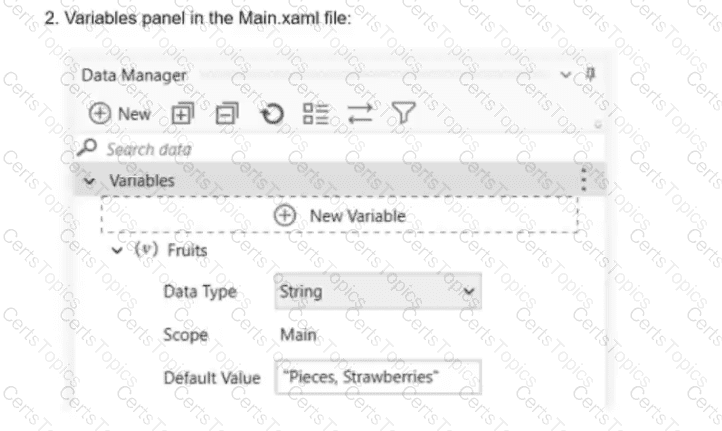
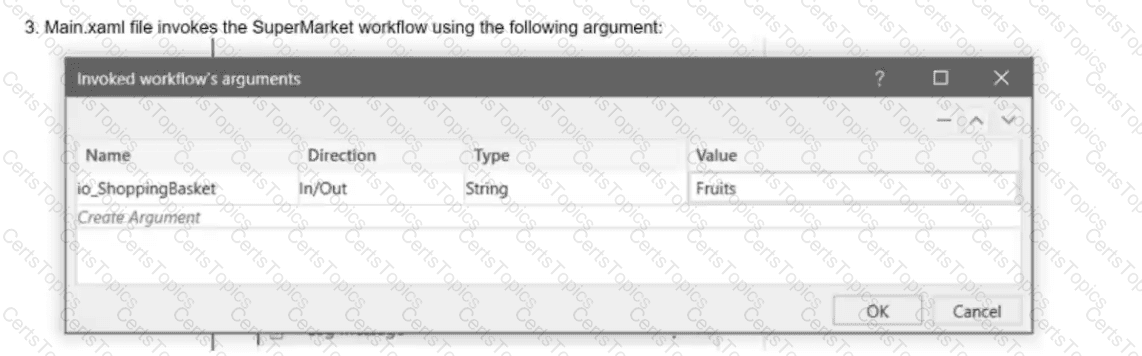
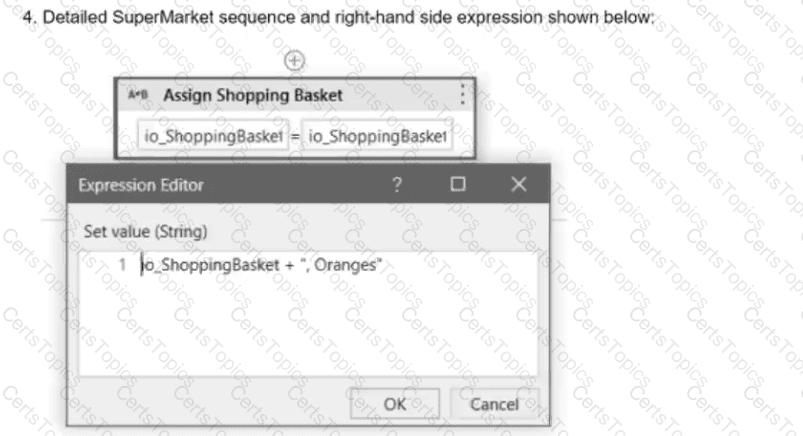
Based on the information shown in the exhibits, what is the output of the Write Line activity in the "Main.xaml" file?
You are developing the MyApp application that has a table, Table A. When the MyApp application is installed on another instance, you want Table A's records to be installed as part of the application. Table A's records will be installed when: