Admission Tests Related Exams
GRE Exam







The term "ragtime opera" was used frequently m the first years of the twentieth century, but more often than not its use was (i)_________. The very idea of "ragtime opera" was viewed as lii)_________: opera was regarded as the highest form of musical art; ragtime was at the opposite pole.
The units digit of 7 is v. and the units digit of 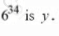 What is the value of the product xy
What is the value of the product xy
Claim: Governments must ensure that their major cities receive the financial support they need in order to thrive.
Reason: It is primarily in cities that a nation's cultural traditions are preserved and generated.
Write a response in which you discuss the extent to which you agree or disagree with the claim and the reason on which that claim is based.