The rule that optimal portfolios will maximize the Sharpe ratio only applies when which of the following conditions is satisfied:
I. It is possible to borrow or lend any amounts at the risk free rate
II. Investors' risk preferences are fully described by expected returns and standard deviation
III. Investors are risk neutral
The LIBOR square swap offers the square of the interest rate change between contract inception and settlement date. If LIBOR at inception is y, and upon settlement is x, the contract pays (x - y)2 for x > y; and -(x - y)2 for x < y.
What of the following cannot be a value of the gamma of this contract?
Which of the following statements are true:
Security A has a beta of 1.2 while security B has a beta of 1.5. If the risk free rate is 3%, and the expected total return from security A is 8%, what is the excess return expected from security B?
Determine the enterprise value of a firm whose expected operating free cash flows are $100 each year and are growing with GDP at 2.5%. Assume its weighted average cost of capital is 7.5% annually.
A portfolio manager desires a position of $10m in physical gold, but chooses to get the exposure using gold futures to conserve cash. The volatility of gold is 6% a month, while that of gold futures is 7% a month. The covariance of gold and gold futures is 0.00378 a month. How many gold contracts should he hold if each contract is worth $100k in gold?
What would be the expected return on a stock with a beta of 1.2, when the risk free rate is 3% and the broad market index is expected to earn 8%?
What would be the total all in price payable on an 5% annual coupon bond quoted at a clean price of $98, where the settlement date is 60 days after the latest coupon payment. Use Act/360 day basis.
The effectiveness of a hedge is determined by which of the following expressions, where ρx,y is the correlation between the asset being hedged and the hedge position:
A)
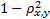
B)
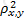
C)
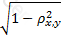
D)
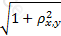
Which of the following statements is not true about covered calls on stocks
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
A digital cash-or-nothing option can be hedged reasonably effectively using:
If the continuously compounded risk free rate is 4% per year, and the continuous rate of dividend on a broad market index is 1% annually, what is the no-arbitrage 6-month futures price of the index if its spot value is $1000?
The risk of a portfolio that cannot be diversified away is called
In terms of notional values traded, which of the following represents the largest share of total traded futures and options globally?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. The convexity of a zero coupon bond maturing in 10 years is more than that of a 4% coupon bond with a modified duration of 10 years
II. The convexity of a bond increases in a linear fashion as its duration is increased
III. Convexity is always positive for long bond positions
IV. The convexity of a zero coupon bond maturing in 10 years is less than that of a 4% coupon bond maturing in 10 years
Determine the price of a 3 year bond paying a 5% coupon. The 1,2 and 3 year spot rates are 5%, 6% and 7% respectively. Assume a face value of $100.
Which of the following is NOT a historical event which serves as an example of a short squeeze that happened in the markets?
The relationship between covariance and correlation for two assets x and y is expressed by which of the following equations (where covarx,y is the covariance between x and y, σx and σy are the respective standard deviations and ρx,y is the correlation between x and y):
A)
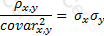
B)
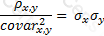
C)
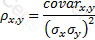
D)
None of the above
Consider a portfolio with a large number of uncorrelated assets, each carrying an equal weight in the portfolio. Which of the following statements accurately describes the volatility of the portfolio?
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT according to CAPM:
A futures clearing house:
A bond has a Macaulay duration of 6 years. The yield to maturity for this bond is currently 5%. If interest rates rise across the curve by 10 basis points, what is the impact on the price of the bond?
Which of the following relationships are true:
I. Delta of Put = Delta of Call - 1
II. Vega of Call = Vega of Put
III. Gamma of Call = Gamma of Put
IV. Theta of Put > Theta of Call
Assume dividends are zero.
A 'consol' is a perpetual bond issued by the UK government. Its running yield is 5%. What is its duration?
If the CHF/USD spot rate is 1.1010 and the one year forward is 1.1040, what is the annualized forward premium or discount, and the one year swap rate?
Which of the following statements is a correct description of the phrase present value of a basis point?
What is the price of a treasury bill with $100 face maturing in 90 days and yielding 5%?
A utility function expresses:
A receiver option on a swap is a swaption that gives the buyer the right to:
Identify the underlying asset in a treasury note futures contract?
A trader finds that a stock index is trading at 1000, and a six month futures contract on the same index is available at 1020. The risk free rate is 2% per annum, and the dividend rate is 1% per annum. What should the trader do?
Which of the following portfolios would require rebalancing for delta hedging at a greater frequency in order to maintain delta neutrality?
The gamma in a commodity futures contract is:
Using a single step binomial model, calculate the delta of a call option where future stock prices can take the values $102 and $98, and the call option payoff is $1 if the price goes up, and zero if the price goes down. Ignore interest.
A refiner may use which of the following instruments to simultaneously protect against a fall in the prices of its products and a rise in the prices of its inputs:
For an investor short a bond, which of the following is true:
I. Higher convexity is preferable to lower convexity
II. An increase in yields is preferable to a decrease in yield
III. Negative convexity is preferable to positive convexity
A zero coupon bond matures in 5 years and is yielding 5%. What is its modified duration?
Which of the following markets are characterized by the presence of a market maker always making two-way prices?
A stock sells for $100, and a call on the same stock for one year hence at a strike price of $100 goes for $35. What is the price of the put on the stock with the same exercise and strike as the call? Assume the stock pays dividends at 1% per year at the end of the year and interest rates are 5% annually.
Which of the following have a negative gamma:
I. a long call position
II. a short put position
III. a short call position
IV. a long put position
The price of a bond will approach its par as it approaches maturity. This is called:
The volatility of commodity futures prices is affected by