Some elderly individuals can have poor dietary habits which can lead to decreased nutrient absorption, including zinc.
A zinc deficiency in the elderly is often caused by:
Charcot-Leyden crystals in stool are thought to be created from damaged eosinophil byproducts. These crystals have a strong association, although they are rare, with parasitic infections or allergic reactions.
Charcot-Leyden crystals in stool may be associated with an immune response and are thought to be the breakdown products of:
Chain-of-Custody procedures must be followed for
The anticoagulant present in a light-blue stopper tube is:
Match each of the following definitions associated with heart disease and heart failure to the term that it defines.
1. Congestive heart failure
2. Infarction
3. Ischemia
4. Angina
Myoglobin release is strongly associated with muscle damage; therfore, it would most closely match a diagnosis of massive muscle trauma in this question.
Myoglobinuria is MOST likely to be noted in urine specimens from patients with which of the following disorders?
Which of the following cardiac biomarkers rises within 30 minutes - 4 hours after chest pain, peaks in 2 - 12 hours, and is usually normal within 24 - 36 hours.
The Bethesda assay is used to measure the titer and activity of the antibody present in a patient's sample. Prothrombin time is an initial screening procedure for bleeding disorders and a test used for monitoring anticoagulant therapy. A thrombin time is used to detect heparin interference in an aPTT mixing study. A mixing study is performed to detect the presence of a factor deficiency or coagulation inhibitor, but does not quantify the result.
Hematology
Which of the following tests is used to quantify a coagulation inhibitor?
The beta hemoglobin chain loci are found on which chromosome?
RAST tests, or Radioallergosorbent tests, are used to screen for an allergy to a specific substance or substances if a person presents with allergy-like symptoms.
The assay which is most helpful in identifying specific allergens is:
Transmission-based precautions isolation categories include all of the following except:
The role of provider-performed microscopy (PPM) is the
CAMP is the correct answer because the case is typical of Streptococcus agalactiae(Group B strep). The main presumptive identification test is CAMP. Bile solubility is positive for Streptococcus pneumonia. Coagulase would be positive for Staphylococcus aureus. PYR is positive for Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A strep) which is ruled out by the resistance to bacitracin.
Microbiology
Spinal fluid cultures on a 3-day-old infant revealed beta-hemolytic, Gram-positive cocci occurring in pairs and chains. The organism was catalase-negative and bile esculin-negative. Resistance to 0.04 U disk of bacitracin was noted. The other test necessary to identify this organism is a positive test by:
When an antigen comes in contact with the skin, the antigen is processed by cells in the epidermis and come in contact with T lymphocytes. T lymphocytes recognize the antigen as foreign and circulate through the bloodstream back to the epidermis and produce an inflammatory response to eliminate the antigen, but this immune response can produce a characteristic rash in the skin called contact dermititis.
Contact dermatitis is mediated by:
Primary- Target glands (such as thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, etc.)
Secondary- Pituitary gland
Tertiary- Hypothalamus
Match the type of endocrine dysfunction with the appropriate organ:
1. Target gland
2. Pituitary gland
3. Hypothalamus
The A and B antigens are present on the red cells of an AB patient. H antigen is a precursor to the ABO antigens.
An individual with type AB blood will demonstrate the complete absence of which of the following antigen sites?
Creatinine clearance tests are utilized to estimate the glomerular function of the kidney. The creatitine clearance calculation is defined as the volume of plasma that is cleared of creatinine by the kidney per unit of time and uses the following formula:
creatinine clearance = Urine creatinine conc x Volume / Plamsa creatinine conc
Creatinine clearance measurements have a recommended specimen requirement = 24-hour urine collection.
Which of the following tests would be useful in the assessment of glomerular filtration:
Malbranchia species share the production of alternate staining arthroconidia as a common feature with the mold form of Coccidioides immitis.
Both Geotrichum species and Trichosporon species produce rectangular-shaped arthroconidia; however, they are regularly rather than alternately staining. Additionally, the arthroconidia of Geotrichum may produce germ tubes from one corner and the arthroconidia of Trichosporon species may produce blastoconidia from adjacent corners, features not shared by either Malbranchia species or Coccidioides immitis.
The hyphae of Microsporum canis, as seen in direct KOH mounts of skin scales, may break up into arthroconidia; however, they are much narrower in dimension and do not share the alternate staining characteristics.
Microbiology
The hyaline saprobic fungus that has microscopic features similar to the mold form of Coccidioides immitis is:
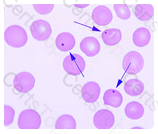
In Rouleaux, red blood cells appear as stacked coins - formation occurs as the result of elevated globulins or fibrinogen.
The RBCs indicated by the arrows in this illustration are the result of:
Polyspecific antihuman globulin (AHG) reagent contains both anti-IgG and anti-C3d.
Polyspecific antihuman globulin (AHG) reagent used in antiglobulin testing should react with which one of the following?
Which of the following is NOT part of the stand or framework of the microscope?
An international, nonprofit organization that establishes standards of best current practice for clinical laboratories is
The purpose of protective isolation is to protect:
Serum amylase and lipase levels may be slightly elevated in chronic pancreatitis, but not diagnostic enough to predict chronic pancreatitis; wheras high levels are found only during acute pancreatitis episodes. In the later stages of chronic pancreatitis, normal to decreased levels of amylase and lipase are caused by the gradual inability of the pancreas to secrete the enzyme
All of the statements below regarding amylase and lipase in pancreatitis are TRUE EXCEPT:
Alkaline over acid, or K/A, in TSI reactions is associated with the fermatation of glucose alone and the utilization of peptone.
Which of the following sugars has been fermented by a gram-negative rod that has produced an alkaline slant and an acid butt on triple sugar iron agar (TSI).?
The morphologic characteristic(s) associated with the Chediak-Higashi syndrome is (are):
Where can one find guidance on the minimum performance standards for clinical laboratories?
Failure to tightly seal specimens for sweat electrolytes during collection and transport will cause:
Albumin is a "negative" acute phase protein since it is found in decreased levels during acute phase response. Alpha-1-antitrypsin, fibrinogen, and ceruloplasmin are all "positive" acute phase proteins that are found in increased levels during acute phase response.
Which one of the following usually shows a decrease during an acute phase response?
The image shown in this question is depicting a rosette formation. Here the red blood cells are surrounding and adhering to the outside of the white blood cell.
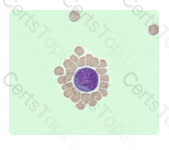
What is the best description of the phenomenon seen in this illustration?
Conversion of only the slant to a pink color in a Christensen's urea agar slant is produced by bacterial species that have weak urease activity. The reaction in the slant to the right is often produced by Klebsiella species, as an example. Strong urease activity is indicated by conversion of the slant and the butt of the tube to a pink color, as seen in the tube to the left. The slant only reaction in the right tube may be seen early on if only the slant had been inoculated; however, with a strong urease producer, both the slant and the butt would turn. Therefore, the reaction is dependent on the strength of urease activity. If the media had outdated for a prolonged period, either there would be no reaction or the appearance of only a faint pink tinge, either in the slant, the butt or both, again depending on the strength of urease production by the unknown organism.
The urease reaction seen in the Christensen's urea agar slant on the far right indicates:

Provide the equivalent measurement for one gallon.
Question options:
1+ reaction has numerous small clumps and cloudy red supernatant
2+ has many medium-sized clumps and clear supernatant.
3+ has several large clumps and clear supernatant
4+ has one solid clump, no free cells, and clear supernatant
BB
Tube-based agglutination reactions in blood bank are graded from negative (0) to 4+. A reaction that has numerous small clumps in a cloudy, red background is:
Molarity x Molecular Weight x Volume = Grams
Molecular Weight (aka Formula Weight) =
2(1) + 32 + 4(16) = 98
So, 4 x 98 x 0.2L = 78.4g
What weight of H2SO4 is contained in 200 ml of a 4 molar H2SO4 solution? (Atomic weight: H= 1; S = 32; 0 = 16)
Which specimen should be collected last?
Question options:
The characteristic that distinguishes vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from other Enterococcus species is their lack of motility.
Enterococci are all catalase-negative. Growth on bile esculin agar and in 6.5% salt broth are two characteristics that have commonly been used to identify Enterococcus to the genus level. A positive esculin in combination with a positive PYR reaction is another approach to presumptive identification.
Which one of these characteristics distinguishes vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from other Enterococcus species?
Only non-self antigens can be immunogenic. Self antigens are normally recognized by the immune system as part of the host, so an immune response does not normally occur. Non-self antigens are immunogenic since they have the potential to cause an immune response.
For a substance to be immunogenic it must be:
The creatinine clearance for this patient is 100 mL/min.
Creatinine clearance values are calculated using the following equation:
Creatinine Clearance (mL / min) = (Urine Creatinine / Serum Creatinine) x Urine Volume (mL) / [ time (hr) x 60 ]
For this patient Creatinine clearance (mL/min)= (120/1.5) x (1800 / [24 x 60])
80 x 1800/1440, which is 80 x 1.25, or 100 mL/min
A 45-year-old male of average height and weight had a serum creatinine of 1.5 mg/dL and urine creatinine was 120 mg/dL; the total volume of urine collected over a 24-hour period was 1,800 mL. Calculate the creatinine clearance for this patient in mL/min.
The results demonstrate compliance with diet and medication. A HbA1C result that is <7.0% indicates glycemic control for most adults with diabetes.
Chemistry
A HbA1C result for a diabetic patient is 6.0%. What conclusion can be made regarding this patient's carbohydrate management?
The electrolyte panel consists of potassium, sodium, chloride, carbon dioxide. These analytes are also typically ordered within other panels as well, including the basic metabolic and complete metabolic panels.
An electrolyte panel (lytes, chem-4) consists of:
Cryptococcus neoformans is the MOST likely identification of the encapsulated yeast in this question. C. neoformans is urease +, and grows brown colonies on birdseed agar. In addition, India ink stain can also be used for Cryptococus spp. identification.
What is the MOST likely identification of an encapsulated yeast in a blood culture bottle from a patient with septicemia with the following additional culture information?:
Failure to produce germ tubes
Urease positive
Produced brown pigment on bird seed agar
The intended response is "transfusion dimorphism". The microcytic, hypochromic erythrocytes suggests iron deficiency anemia. Interspersed among these cells are normocytic, normochromic erythrocytes suggesting two populations of red cells following transfusion. This was a case of severe iron deficiency treated with red cell transfusions and iron supplement.
The condition most likely associated with the peripheral blood picture in the photograph is:
Blood Bank
What other component(s) can be shipped together with Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)?
Urinalysis & Other Body Fluids
Match the following urine chemical reagent strip test pads to the disease or disorder that would most likely cause a positive test result.
1. Ketones
2. Blood
3. Bilirubin
4. Nitrites
Healthcare workers that worked closely with patient specimens were at an increased risk of contracting which viral infection before a vaccine was developed?
Which of the following genotypes cause beta thalassemia minor?
Though it may not be required, TDM should still be used to confirm adequate dosing. Genotyping does not make TDM redundant.
A PM will metabolize the drug more slowly and therefore will need lower doses. CYP2D6 metabolizes many different drugs; it is not associated with just one class of drugs. Anytime a drug is taken that competes for the same metabolizing enzyme as another drug, there is potential for the concentrations of both drugs to be increased.
A patient has been characterized as a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer (PM) after genotyping. Which of the following statements is not true?
What are the certification requirements for clinical laboratory professionals?
The concentration of circulating ferritin is proportional to the size of iron stores.
Which of the following will give the best overall picture of a patient's iron stores:
PCT usually rises within 3-6 hours of infection. CRP also increases rapidly following infection, but is not as specific for infection as PCT. A rise in CRP could also occur with SIRS. Lactic acid is usually used to detect and monitor impaired circulation and tissue oxygenation in critically ill patients.
Chemistry
Of the three laboratory tests that are listed, which has proven to be most effective for early differentiation of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) from sepsis due to its increase following infection and higher specificity?
Provide the equivalent measurement for one pint.
Post-hepatic obstruction is characterized by a marked increase in alkaline phosphatase, GGT, conjugated bilirubin, as well as other hepatic enzymes. The slight rise of ALT suggests that the issue is not hepatitis. Renal and cardiovascular failure do not match the symptom of jaundice or the abnormal laboratory values.
Chem
Which of the following conditions would be suggested by a jaundiced patient experiencing a marked rise in alkaline phosphatase, conjugated bilirubin, and a slight rise in ALT:
Secondary granules, also known as specific granules first appear in the myelocyte stage next to the nucleus. In neutrophils this is termed the "dawn of neutrophilia".
What is one of the main characteristics of secondary granules in the neutrophilic granulocyte cytoplasm?
Convert the following temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius
102 degrees F
Since cimetidine inhibits CYP2D6, less amphetamine will probably need to be given since it will not be able to be metabolized as readily.
Most drug interactions are like this: one drug inhibits or competes with the same CYP450 as another drug. The end result is that higher concentrations of one, or both, drugs are present, leading to potential toxicity.
A patient is taking cimetidine for a stomach ulcer. This drug inhibits CYP2D6. The patient is now prescribed amphetamine for narcolepsy. Amphetamine is metabolized by CYP2D6. What would you predict?
Microbiology
Matching: The detection of a distinct odor is often helpful in the presumptive identification of bacterial culture isolates. Match each of the odors listed with its corresponding bacterial species name.
1. Streptococcus anginosus (milleri)
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Eikenella corrodens
4. Alcaligenes faecalis
The Westgard multi-rule 22S describes the scenario where two consecutive data points fall outside +2SD or -2SD. If this occurs, then the run must be rejected. This situation is most likely caused by a systematic error.
Which of the following describes the Westgard multi-rule 22S?
The color coding of evacuated tubes provides information about all of the following except the: Question options:
Plasma concentrations of creatinine are used to assess renal function. Creatinine clearance is based on the serum creatinine level and is used to measure glomerular filtration rate, or GFR.
An increased serum level of which of the following analytes is MOST commonly associated with decreased glomerular filtration?
If your reactions are strong at immediate spin (3+) and then get weaker at AHG (w+), it could mean the presence of a strong cold antibody.
Cold antibodies tend to be IgM and their optimum phase for reactivity is immediate spin. Incubation and washing of the sample may cause the agglutination that occurred at room temperature to break down. This would appear as a weaker reaction at AHG.
If the reaction strengths varied in each panel cell then that could be an indication that there are multiple antibodies present.
Your screen cells are 3+ at immediate spin and weak (W)+ at AHG. Your auto control is negative for both phases. Some of your antibody panel cells are 3+ at immediate spin and negative at AHG. What should you suspect?
What component is indicated for patients who receive directed donations from immediate family members to prevent transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD)?
Cerebrospinal fluid has three main functions:
Protect brain and spinal cord from trauma.
Supply nutrients to nervous system tissue.
Remove waste products from cerebral metabolism.
Which of the following are functions of CSF? Please select all correct answers
The steps in the PCR process are:
1. Denaturation (Turning double stranded DNA into single strands.)
2. Annealing/Hybrization (Attachment of primers to the single DNA strands.)
3. Extension (Creating the complementary strand to produce new double stranded DNA.)
What is the first step of the PCR reaction?
Vitamin K is needed to produce certain coagulation factors, in particular factors II, VII, IX, and X. Deficiencies in these factors can lead to increased clotting times and can cause hemorrhagic disease.
A deficiency in which of these vitamins leads to increased clotting time and may result in hemorrhagic disease?
When making a platelet concentrate, the proper procedure is to start with a low centrifugation of the whole blood bag. After the plasma is removed, it is centrifuged again at a higher speed to separate the platelet portion from the plasma portion.
Blood bank
The following steps must be followed in preparation of a platelet concentrate:
Blood Bank; Immunology
Which of the following best describes the primary function of antibodies:
G6PD deficiency causes an increased suseptibility to the oxidation of hemoglobin, which in turn, causes the precipitation of hemoglobin inside of the red blood cell.
Which one of the following conditions is associated with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency?
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of DNA and appear as small round ball-like inclusions inside the red cells. Usually only one Howell-Jolly body will be present in each red cell.
Single erythrocyte inclusions which are large, round, smooth and purplish-blue staining are most likely:
Insulin is the hormone that is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production
Glucagon and epinephrine promote glycogenolysis, conversion of glycogen to glucose, which increases plasma glucose. Cortisol, along with glucagon, increases gluconeogenesis, formation of glucose from noncarbohydrates, which also raises plasma glucose concentration.
Chemistry
Which of the following hormones is mainly responsible for the entry of glucose into the cell for energy production?
Serum amylase and lipase levels may be slightly elevated in chronic pancreatitis, but not diagnostic enough to predict chronic pancreatitis; wheras high levels are found only during acute pancreatitis episodes. In the later stages of chronic pancreatitis, normal to decreased levels of amylase and lipase are caused by the gradual inability of the pancreas to secrete the enzyme
All of the statements below regarding amylase and lipase in pancreatitis are TRUE EXCEPT:
Elevation in conjugated bilirubin is most likely to be found in which of the following conditions:
Basophilic stippling is strongly associated with lead poisoning the lead toxicity can affect the bone marrow; causing this phenomenon.
Hematology
What is a prominent morphologic feature of lead poisoning:
The best course of action when entering an isolation room is:
Entamoeba gingivalis resembles Entamoeba histolytica both in size and in nuclear characteristics. Entamoeba gingivalis may contain numerous cytoplasmic inclusions such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria.
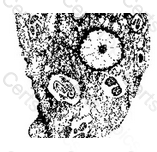
I reside in the mouth where I measure approximately 17 micro meters.
Serum calcitonin is normally produced by the C cells of the thyroid. It functions to reduce serum calcium by inhibiting release of calcium from bone. It is a peptide with a molecular weight of 3400, and has a half life of approximately 12 minutes. It is characteristically elevated in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Since medullary carcinoma often occurs as an autosomal disorder, family members of patients with this condition should be screened for serum calcitonin.
Serum calcitonin is typically elevated in which of the following conditions:
The personal protective equipment (PPE) that is used in the laboratory to protect the personnel when performing tests on patient blood samples is which of the following:
What two glycoproteins are expressed on the surface of influenza A viruses and are used for subtyping of the viruses?
High triglycerides may be caused by disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypothyroidism, Cushing's sydnrome, liver disease, uremia, dysglobulinemia, nephrotic syndrome, and alcoholism can cause hypertriglyceridemia.
A 46-year old known alcoholic with liver damage is brought in the ER unconscious. One would expect his lipid values to be affected in what way?
In the laboratory, surfaces must be disinfected for blood spills. What is the most common disinfectant used?
An ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) would require a higher dose of a drug than an EM (a person with normal enzyme activity) since the UM eliminates the drug more quickly.
A CYP2D6 ultrarapid metabolizer (UM) would require ___________ dose of an active drug (non-prodrug) that is metabolized by CYP2D6 than a CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer (EM).
Antidiuretic hormone, or ADH, has the important role of conserving body water by reducing the loss of water in urine by changing the water permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct. An increase in ADH causes a concentrated urine since the water is retained and absorbed through the permeable membrane. An decrease in ADH causes the collecting ducts to retain very little water, instead it is excreted as urine.
Chemistry
Which of the following action describes the MAJOR property of antidiuretic hormone?
% concentration (expressed as a proportion or ratio) x volume needed = mass of reagent to use
So... 10% (w/v) solution of sodium hydroxide x 200 mL needed = 20 grams of sodium hydroxide
How many grams of sodium hydroxide are required to prepare a 200 ml solution of a 10% (weight per volume) solution? (Atomic weights: Na = 23; 0 = 16; H = 1)
Western blot analysis is frequently utilized as the confirmatory method of HIV detection.
Which of the following assays is routinely used for confirmation of HIV infections:
HLA-DR is a class II MHC.
HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C are all class I MHC.
Which of the following antigens is classified as a Major Histocompatibility Complex
Class II antigen (MHCII)?
Platelet neutralization tests are one of the confirmatory tests that can be used to determine if a patient has a circulating lupus antibody, or lupus anticoagulant. The principle in this test involved the use of a freeze-thawed platelet suspension that, when mixed with the patient plasma, will neutralize the anti-phospholipid antibodies (lupus anticoagulant) present and allow for a corrected aPTT result upon re-testing.
A patient has a history of repeated spontaneous abortion. Coagulation studies reveal an elevated APTT, normal PT, normal platelet function, and normal clotting time. Schistocytes were seen on the peripheral blood smear.
Which test should be performed to determine if the patient has lupus anticoagulant?