Which system control adjusts amplification of signals as a function of depth?
Which color control was adjusted in color bar A to produce color bar B?

What is an advantage of power Doppler over color Doppler?
Which artifact is seen as a result of an increase in echo amplitude in the tissue located distal to an anechoic structure?
Which process is used to fill in blank spaces between scan lines?
What is the most effective way to reduce aliasing on color Doppler?
Which control should a sonographer use to change contrast resolution?
Which factor does a string phantom evaluate?
What improves the temporal resolution of color flow imaging?
What causes color flash artifact?
Which type of display process rescans only the region of interest and improves resolution?
Which characteristic of ultrasound transmission is directly proportional to an increase in frequency?
Which will affect the gray-scale of a 2-D image?
Which statement describes the purpose of using a spectral Doppler wall filter?
According to Poiseuille's law, a change in which parameter would have the greatest influence on blood flow?
Which factor affects lateral resolution in ultrasound?
What is the purpose of applying compression to the received signals?
Which can cause color aliasing?
Which component of a contrast agent causes a marked mismatch in impedance between the agent and blood?
What is the term for the change in direction of a sound wave crossing a tissue boundary at an oblique angle?
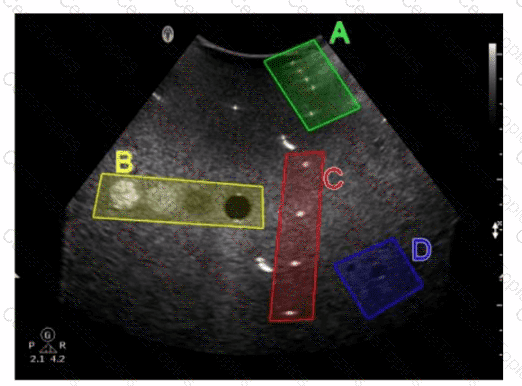
Which target group in this image of a tissue-mimicking phantom is used for gray-scale evaluation?
Which adjustment follows the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle of patient safety?
Which feature is a characteristic of continuous wave Doppler?
Which artifact is caused by defects in the crystals of the transducer?
Which resolution is degraded with multiple electronic foci?
Which describes the reflected frequency when a reflector is moving toward the sound source?
Which resolution capability is most affected by spatial pulse length?
Which index is related to the likelihood of cavitation?
Which artifact results from decreased attenuation?
Which function is the purpose of the matching layer?
Which adjustment can maintain the same frame rate when the depth is increased?
Which transducer was most likely used to create this image?
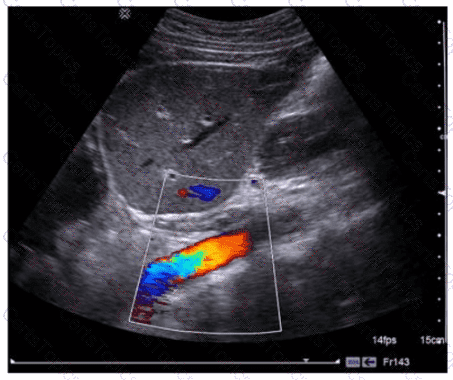
Which effect does spatial compounding have on ultrasound images?
What is the term for an ultrasound system's ability to display low-level echoes?
For harmonic imaging, what must the overall transducer bandwidth contain?
Which factor influences color flow imaging frame rate?
Which adjustment improves temporal resolution?
What is the effect of increasing the overall gain?
Which action is the first step for the removal of visible contaminants from the transducer?
How is intensity of an ultrasound beam measured?
Which target group in this image of a tissue-mimicking phantom is used to evaluate axial resolution?
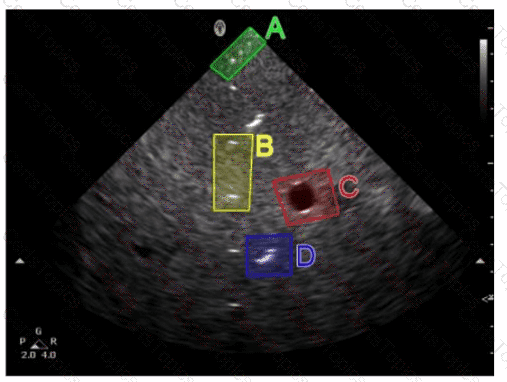
Which unfocused transducer will have the greatest divergence?
Which technique averages individual frames together to improve the image?
What is assessed with power Doppler?
Which technique uses frame averaging?
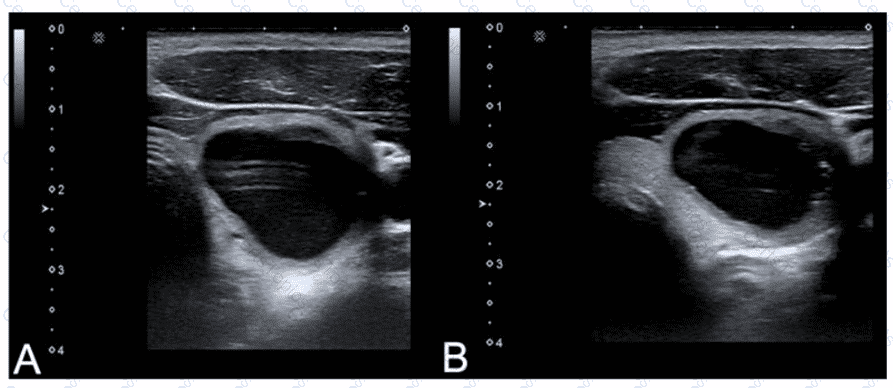
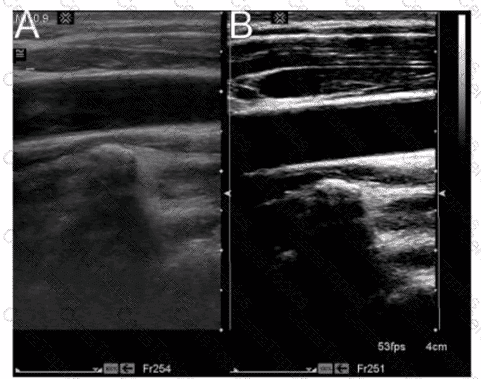
Which adjustment will reduce the artifact in the cystic lesion in image A resulting in image B?
What is the effect of an increased aperture in a linear array transducer?
Which technique averages image frames over time to reduce noise?
What is an advantage of pulsed-wave Doppler over continuous-wave Doppler?
Which statement characterizes the primary difference between image A and image B?
What limits the maximum imaging depth for a given transducer?
Which factor will improve axial resolution?
Which color Doppler control allows for reassignment of red and blue to represent flow direction?
What is the primary reason to use compression?