Which pathology is demonstrated in this video clip?
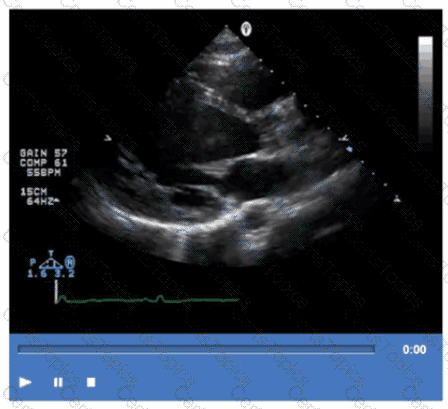
Which finding is most commonly associated with Ebstein anomaly?
When should a patient's systemic blood pressure be documented on an echocardiogram?
Which type of mass is typically attached to the fossa ovalis of the left atrium?
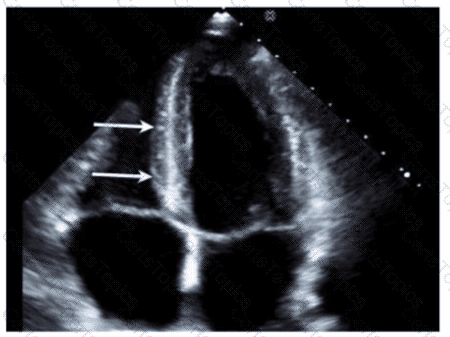
Which wall is indicated by the arrows on this image?
Based on this video, what is the estimated right atrial pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg)?
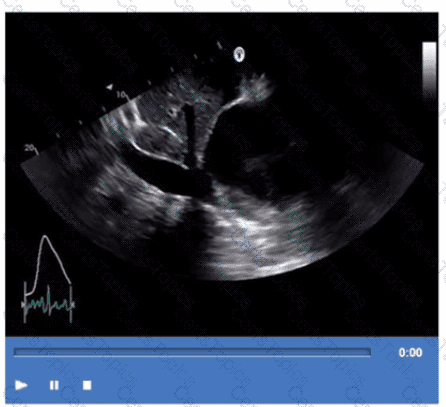
Which Doppler signal is most consistent with significant aortic valve regurgitation?
Which method of measuring left atrial size is most recommended and most accurate?
Which adjustment is most likely to improve image quality from the suprasternal long axis window?
Which finding is indicated by the arrow on this image?

Which congenital heart anomaly is found in approximately 30% of normal adults?
Which next step is appropriate after obtaining the Doppler signal in this image?
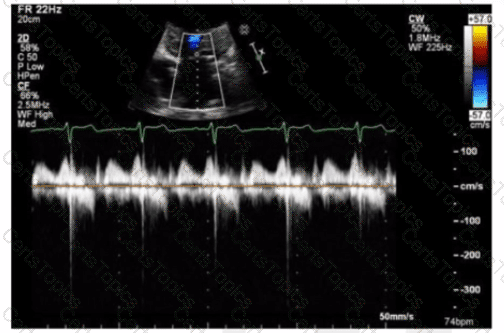
The sonographer obtains this Doppler signal while using the non-imaging transducer in the apical position. What is the best way to differentiate between mitral regurgitation and aortic stenosis signals in the waveform shown in this image?
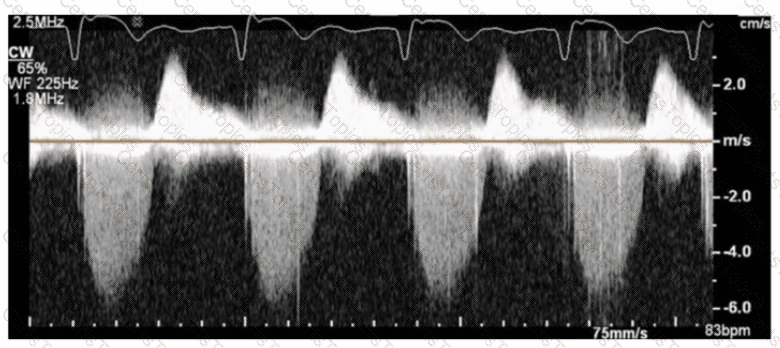
Which finding is NOT associated with severe mitral valve regurgitation?
What is a normal response to dobutamine stress testing?
What is the incidental finding seen by color Doppler in this four-chamber view of a patient with left atrial enlargement?

What potential source of error is the greatest when calculating the aortic valve area by the continuity equation?
Which of the following is the most likely cause for the findings demonstrated in this video?
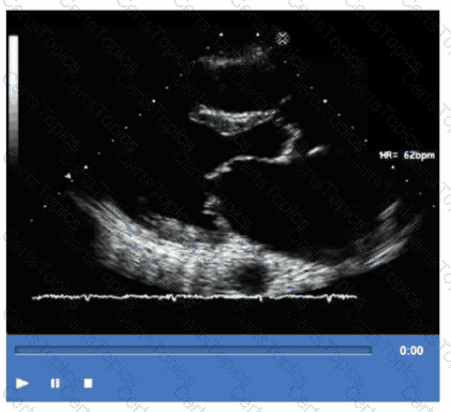
Which of the following conditions will increase in seventy with Valsalva maneuver?
Identify the right pulmonary artery.
Using your mouse, place the cursor on the appropriate region of the image and then left click the mouse button to indicate your selection.
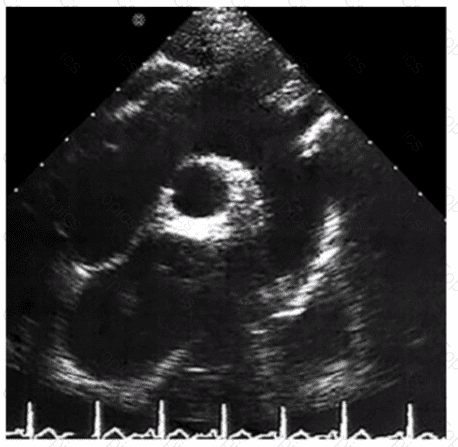
Which mitral regurgitation jet direction is most consistent with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy?
Which hepatic vein flow pattern signals severe tricuspid regurgitation?
Which view is most appropriate for measuring right ventricular dimensions?
Which syndrome is associated with pulmonic stenosis?
The variables necessary to calculate mitral regurgitant (MR) effective orifice area by the proximal isovelocity surface area (PISA) equation include MR aliasing hemispheric radius, the aliasing velocity, and which other parameter?
What is the normal dP/dt value of left ventricular systolic function?
Which of the following is a feature of constrictive pericarditis?
Which flow abnormality produces a continuous murmur?
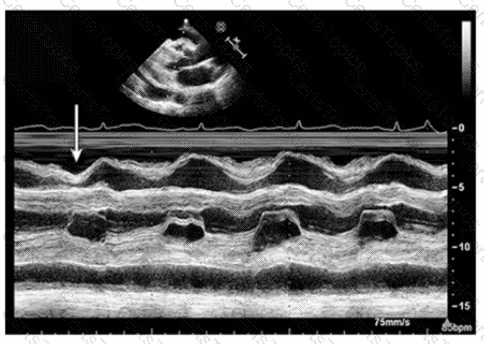
Which condition is most likely demonstrated by this M-mode image?

A patient with a ventricular septal defect, an atrial septal defect, and a cleft mitral valve is likely to have which abnormality?
Which color Doppler adjustment would optimize visualization of flow across the interatrial septum?
Which view is best used to evaluate a bicuspid aortic valve?
Which echocardiography assessment requires mitral inflow pulsed wave, pulmonary venous pulsed wave, and tissue Doppler of the mitral annulus?
The 'P' wave of an electrocardiogram relates to which echocardiography event?
Which of the following can be calculated from the peak tricuspid regurgitant velocity?
Which critical finding is most likely to require immediate surgical intervention?
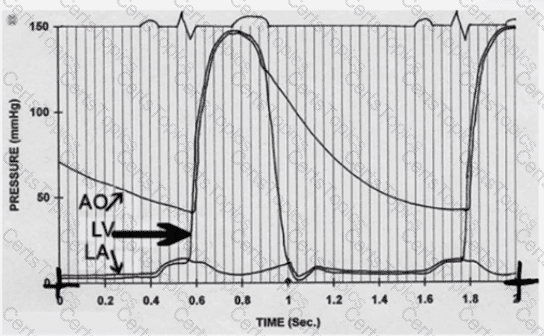
Which valvular pathology is illustrated in this left heart pressure tracing?
An intravenous drug user presents with a fever of unknown origin, flu-like symptoms, dyspnea, and chest pain. Which ultrasound finding is mostly likely associated with this presentation?
Which condition is commonly associated with cardiac tamponade?
Which diagnosis is most consistent with the findings in these images?
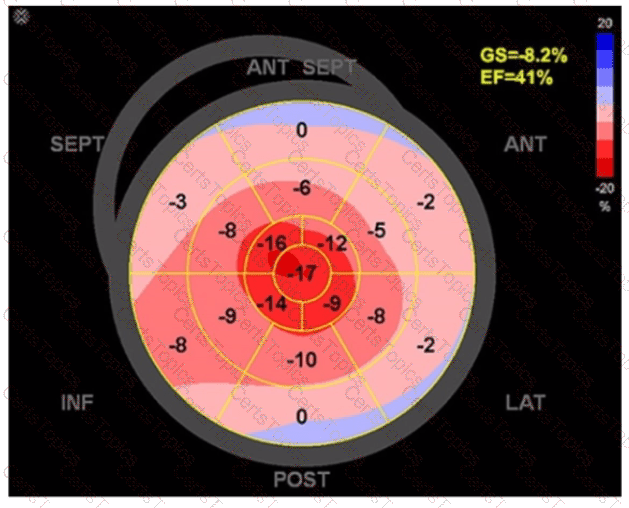
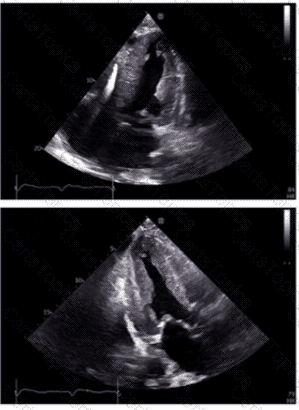
Which condition is most plausible based on the finding indicated by the arrow on this image?